RT-LAMP Multicenter Study for SARS-CoV-2 Genome Molecular Detection in Brazilian Swab and Saliva Samples
- PMID: 36673025
- PMCID: PMC9858473
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13020210
RT-LAMP Multicenter Study for SARS-CoV-2 Genome Molecular Detection in Brazilian Swab and Saliva Samples
Abstract
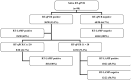
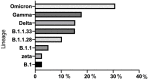
Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) is a rapid method that can replace RT-qPCR. A simple molecular assay for SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection in gold-standard diagnosis through swabs and alternative specimens such as saliva could be helpful in promoting genomic surveillance. A multicenter study was conducted to evaluate the RT-LAMP assay method as an alternative for the molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2 lineages in swab and saliva samples. A total of 350 swabs from individuals with (n = 276) or without (n = 74) COVID-19 tested by RT-qPCR were collected. Paired saliva was also collected from 90 individuals who had SARS-CoV-2 RNA that was detectable (n = 30) or undetectable (n = 60) via RT-qPCR. For the RT-LAMP methodology, six primers were used for ORF1 gene amplification. As for SARS-CoV-2 genotyping, 39 swabs had the whole genome sequenced by MinION. The sensitivity of RT-LAMP to the swab was 90.2%. For the swab samples with Ct ≤ 30, the sensitivity improved by 96%. Considering saliva with Ct ≤ 30 in RT-qPCR testing, the RT-LAMP sensitivity was 100%. The RT-LAMP specificity was 100% for both the swab and saliva samples. This RT-LAMP assay was capable of detecting all the SARS-CoV-2 lineages circulating in the Brazilian swab samples. The RT-LAMP method has significant potential for use in clinical routines since it was capable of detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA in swab and saliva samples.
Keywords: COVID-19; LAMP; SARS-CoV-2; diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reverse-Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Has High Accuracy for Detecting Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Saliva and Nasopharyngeal/Oropharyngeal Swabs from Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Individuals.J Mol Diagn. 2022 Apr;24(4):320-336. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2021.12.007. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Mol Diagn. 2022. PMID: 35121140 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Clinical Application of a Rapid and Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Test for SARS-CoV-2 Infection.mSphere. 2020 Aug 26;5(4):e00808-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00808-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32848011 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Ultrasensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva and Viral Transport Medium Clinical Samples.Anal Chem. 2021 Jun 8;93(22):7797-7807. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05170. Epub 2021 May 25. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34033472
-
Evaluation of saliva as a complementary technique to the diagnosis of COVID-19: a systematic review.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2021 Jul 1;26(4):e526-e532. doi: 10.4317/medoral.24424. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2021. PMID: 33609022 Free PMC article.
-
Salivette, a relevant saliva sampling device for SARS-CoV-2 detection.J Oral Microbiol. 2021 Apr 30;13(1):1920226. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2021.1920226. J Oral Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33986939 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Colorimetric RT-LAMP for SARS-CoV-2 detection from nasopharyngeal swabs or crude saliva: a multicountry diagnostic accuracy study in Africa.Lancet Glob Health. 2025 Jul;13(7):e1258-e1267. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(25)00150-0. Lancet Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40580991 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse transcription loop‑mediated isothermal amplification has a high performance in the detection of SARS‑CoV‑2 in saliva samples and nasal swabs from asymptomatic and symptomatic individuals.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Jul 6;26(2):398. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12097. eCollection 2023 Aug. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37522063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 16 September 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous