Immunotherapy Assessment: A New Paradigm for Radiologists
- PMID: 36673112
- PMCID: PMC9857844
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13020302
Immunotherapy Assessment: A New Paradigm for Radiologists
Abstract
Immunotherapy denotes an exemplar change in an oncological setting. Despite the effective application of these treatments across a broad range of tumors, only a minority of patients have beneficial effects. The efficacy of immunotherapy is affected by several factors, including human immunity, which is strongly correlated to genetic features, such as intra-tumor heterogeneity. Classic imaging assessment, based on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is useful for conventional treatments, has a limited role in immunotherapy. The reason is due to different patterns of response and/or progression during this kind of treatment which differs from those seen during other treatments, such as the possibility to assess the wide spectrum of immunotherapy-correlated toxic effects (ir-AEs) as soon as possible. In addition, considering the unusual response patterns, the limits of conventional response criteria and the necessity of using related immune-response criteria are clear. Radiomics analysis is a recent field of great interest in a radiological setting and recently it has grown the idea that we could identify patients who will be fit for this treatment or who will develop ir-AEs.
Keywords: Recist 1.1; i-Recist; immuno-related adverse events; immunotherapy; radiological response assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
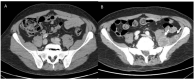
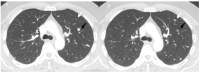
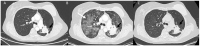
References
-
- Merlotti A., Bruni A., Borghetti P., Ramella S., Scotti V., Trovò M., Chiari R., Lohr F., Ricardi U., Bria E., et al. Sequential chemo-hypofractionated RT versus concurrent standard CRT for locally advanced NSCLC: GRADE recommendation by the Italian Association of Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology (AIRO) Radiol. Med. 2021;126:1117–1128. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01362-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

