Standardized Uptake Values on SPECT/CT: A Promising Alternative Tool for Treatment Evaluation and Prognosis of Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumours
- PMID: 36673128
- PMCID: PMC9857822
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13020318
Standardized Uptake Values on SPECT/CT: A Promising Alternative Tool for Treatment Evaluation and Prognosis of Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumours
Abstract
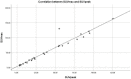
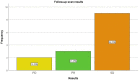
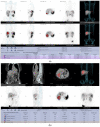
(1) Background: The aim of our study was to assess the feasibility of 99mTcEDDA/HYNIC-TOC SPECT/CT quantitative analysis in evaluating treatment response and disease progression in patients with NETs. (2) Methods: This prospective monocentric study evaluated 35 SPECT/CT examinations performed on 14 patients with neuroendocrine tumours who underwent a baseline and at least one follow-up 99mTcEDDA/HYNIC-TOC scan as part of their clinical management. The examination protocol included a whole-body scan acquired 2 h after the radiotracer’s administration, with the SPECT/CT performed 4 h post-injection. Images were analyzed by two experienced physicians and patients were classified into response categories based on their changes in SUV values. (3) Results: We evaluated 14 baseline studies and 21 follow-up scans, accounting for 123 lesions. A statistically positive correlation has been found between the SUVmax and SUVpeak values in tumoral lesions (p < 0.05). No correlation has been found between the SUV values and the ki67 proliferation index. Finally, 64.29% patients were classified as SD at the end of the study, with only 14.29% of patients exhibiting PD and 21.43% patients with PR. (4) Conclusions: The quantitative analysis of 99mTcEDDA/HYNIC-TOC SPECT/CT data in patients with neuroendocrine tumours could represent an alternative to 68Ga-DOTA-peptides PET/CT for the monitoring and prognosis of NETs.
Keywords: 68Ga-DOTA-PET/CT; 99mTcEDDA/HYNIC-TOC; SPECT/CT; metastatic disease; neuroendocrine tumors; quantitative SPECT/CT; somatostatin receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rindi G., Klimstra D.S., Abedi-Ardekani B., Asa S.L., Bosman F.T., Brambilla E., Busam K.J., de Krijger R.R., Dietel M., El-Naggar A.K., et al. A Common Classification Framework for Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: An International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and World Health Organization (WHO) Expert Consensus Proposal. Mod. Pathol. 2018;31:1770–1786. doi: 10.1038/s41379-018-0110-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nagtegaal I.D., Odze R.D., Klimstra D., Paradis V., Rugge M., Schirmacher P., Washington K.M., Carneiro F., Cree I.A., the WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board The 2019 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System. Histopathology. 2020;76:182–188. doi: 10.1111/his.13975. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

