Reconstruction of the Temporal Correlation Network of All-Cause Mortality Fluctuation across Italian Regions: The Importance of Temperature and Among-Nodes Flux
- PMID: 36673162
- PMCID: PMC9858294
- DOI: 10.3390/e25010021
Reconstruction of the Temporal Correlation Network of All-Cause Mortality Fluctuation across Italian Regions: The Importance of Temperature and Among-Nodes Flux
Abstract
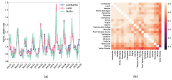
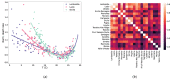
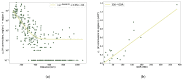
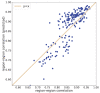
All-cause mortality is a very coarse grain, albeit very reliable, index to check the health implications of lifestyle determinants, systemic threats and socio-demographic factors. In this work, we adopt a statistical-mechanics approach to the analysis of temporal fluctuations of all-cause mortality, focusing on the correlation structure of this index across different regions of Italy. The correlation network among the 20 Italian regions was reconstructed using temperature oscillations and traveller flux (as a function of distance and region's attractiveness, based on GDP), allowing for a separation between infective and non-infective death causes. The proposed approach allows monitoring of emerging systemic threats in terms of anomalies of correlation network structure.
Keywords: complex networks; dynamical systems; epidemiology; time series.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- English L.K., Ard J.D., Bailey R.L., Bates M., Bazzano L.A., Boushey C.J., Brown C., Butera G., Callahan E.H., De Jesus J., et al. Evaluation of dietary patterns and all-cause mortality: A systematic review. JAMA Netw. Open. 2021;4:e2122277. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.22277. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Foster H.M., Celis-Morales C.A., Nicholl B.I., Petermann-Rocha F., Pell J.P., Gill J.M., O’Donnell C.A., Mair F.S. The effect of socioeconomic deprivation on the association between an extended measurement of unhealthy lifestyle factors and health outcomes: A prospective analysis of the UK Biobank cohort. Lancet Public Health. 2018;3:e576–e585. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(18)30200-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martinez G.S., Diaz J., Hooyberghs H., Lauwaet D., De Ridder K., Linares C., Carmona R., Ortiz C., Kendrovski V., Adamonyte D. Cold-related mortality vs heat-related mortality in a changing climate: A case study in Vilnius (Lithuania) Environ. Res. 2018;166:384–393. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.06.001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

