Transcriptome and Proteome Analysis Revealed the Influence of High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunits (HMW-GSs) Deficiency on Expression of Storage Substances and the Potential Regulatory Mechanism of HMW-GSs
- PMID: 36673453
- PMCID: PMC9857648
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12020361
Transcriptome and Proteome Analysis Revealed the Influence of High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunits (HMW-GSs) Deficiency on Expression of Storage Substances and the Potential Regulatory Mechanism of HMW-GSs
Abstract
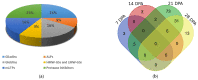
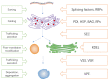
The processing quality of wheat is affected by seed storage substances, such as protein and starch. High-molecular-weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GSs) are the major components of wheat seed storage proteins (SSPs); they are also key determinators of wheat end-use quality. However, the effects of HMW-GSs absence on the expression of other storage substances and the regulation mechanism of HMW-GSs are still limited. Previously, a wheat transgenic line LH-11 with complete deletions of HMW-GSs was obtained through introducing an exogenous gene Glu-1Ebx to the wild-type cultivar Bobwhite by transgenic approach. In this study, comparative seed transcriptomics and proteomics of transgenic and non-transgenic lines at different seed developmental stages were carried out to explore the changes in genes and proteins and the underlying regulatory mechanism. Results revealed that a number of genes, including genes related to SSPs, carbohydrates metabolism, amino acids metabolism, transcription, translation, and protein process were differentially enriched. Seed storage proteins displayed differential expression patterns between the transgenic and non-transgenic line, a major rise in the expression levels of gliadins were observed at 21 and 28 days post anthesis (DPA) in the transgenic line. Changes in expressions of low-molecular-weight glutenins (LMW-GSs), avenin-like proteins (ALPs), lipid transfer proteins (LTPs), and protease inhibitors (PIs) were also observed. In addition, genes related to carbohydrate metabolism were differentially expressed, which probably leads to a difference in starch component and deposition. A list of gene categories participating in the accumulation of SSPs was proposed according to the transcriptome and proteome data. Six genes from the MYB and eight genes from the NAC transcription families are likely important regulators of HMW-GSs accumulation. This study will provide data support for understanding the regulatory network of wheat storage substances. The screened candidate genes can lay a foundation for further research on the regulation mechanism of HMW-GSs.
Keywords: HMW-GSs; candidate genes; regulation mechanism; seed storage substances; wheat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Meziani S., Nadaud I., Tahir A., Nurit E., Benguella R., Branlard G. Wheat aleurone layer: A site enriched with nutrients and bioactive molecules with potential nutritional opportunities for breeding. J. Cereal Sci. 2021;100:103225. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2021.103225. - DOI
-
- Jiang P., Gao J., Zheng X., Feng J., Xue J., Duan L., Gu Y., Li Y., Yan Y., Li X. Clustered Transcription Initiators and Expression of HMW-GS Genes in Wheat Endosperm. Crop Sci. 2017;57:378–386. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2016.07.0571. - DOI
-
- León E., Marín S., Giménez M.J., Piston F., Rodríguez-Quijano M., Shewry P.R., Barro F. Mixing properties and dough functionality of transgenic lines of a commercial wheat cultivar expressing the 1Ax1, 1Dx5 and 1Dy10 HMW glutenin subunit genes. J. Cereal Sci. 2009;49:148–156. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2008.08.002. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2022KJCXZX-LYS-1/HAAFS Science and Technology Innovation Special Project
- 2022KJCXZX-LYS-20/HAAFS Science and Technology Innovation Special Project
- 2023KJCXZX-LYS-GH02/HAAFS Science and Technology Innovation Special Project
- 20326345D/Science and Technology Program of Hebei
- C2022301004/Science and Technology Program of Hebei
- HBCT2018010201/Hebei Modern Agricultural Industrial Technology System
- 21326318D/Project for Hebei Scientific and Technological Innovation Team of Modern Wheat Seed Industry
- C21R0303/Talents construction project of science and technology innovation, HAAFS
- C22R0305/Talents construction project of science and technology innovation, HAAFS
- 2021YFD1200601/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

