From Zero to Hero: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Hike on the Way of St. James-A Feasibility Study with Analyses of Patients' Quality of Life, Diabetes Distress and Glucose Profile
- PMID: 36674186
- PMCID: PMC9861500
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20021417
From Zero to Hero: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Hike on the Way of St. James-A Feasibility Study with Analyses of Patients' Quality of Life, Diabetes Distress and Glucose Profile
Abstract
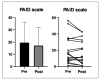
This study investigates the feasibility of an accompanied 5-day hiking tour (Way of St. James) for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients and its impact on their quality of life/well-being, diabetes distress and glucose profile. Twenty-three T2DM patients (with and without insulin therapy) participated in the study. The 120 km pilgrimage (from Ferrol to Santiago de Compostela, Spain) was accompanied by three physicians, two diabetes counselors and one sports scientist. Quality of life/well-being was assessed by the World Health Organization’s (WHO)-5 questionnaire, and diabetes distress was evaluated based on the Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) scale. The glucose levels of six insulin-treated patients were measured using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, considering that insulin-treated patients can be at increased risk of exercise-induced hypoglycemia. A significant improvement in quality of life/well-being was reported (p < 0.001), while diabetes distress did not change significantly (p = 0.203). Only two of the six insulin-treated patients showed moderate hypoglycemic episodes between 0.97% and 5.21% time below range per day, with glucose levels between 53−70 mg/dL. Hiking tours such as the one organized for this study can improve quality of life/well-being without increasing diabetes distress and are considered relatively safe for T2DM patients, even for those being treated with insulin.
Keywords: continuous glucose monitoring; diabetes; diabetes distress; glucose profile; hiking; pilgrimage; quality of life; well-being.
Conflict of interest statement
H.P.K. is a member of the Lilly Advisory Board. U.B. received lecture fees from Lilly. S.K. received lecture fees from Abbott. C.B. is a member of the Abbott Advisory Board. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2021.
-
- González-Castro T.B., Escobar-Chan Y.M., Fresan A., López-Narváez M.L., Tovilla-Zárate C.A., Juárez-Rojop I.E., Ble-Castillo J.L., Genis-Mendoza A.D., Arias-Vázquez P.I. Higher Risk of Depression in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: Results of a Meta-Analysis. J. Health Psychol. 2021;26:1404–1419. doi: 10.1177/1359105319876326. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nouwen A., Adriaanse M.C., van Dam K., Iversen M.M., Viechtbauer W., Peyrot M., Caramlau I., Kokoszka A., Kanc K., de Groot M., et al. Longitudinal Associations between Depression and Diabetes Complications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabet. Med. 2019;36:1562–1572. doi: 10.1111/dme.14054. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

