Tailored PGE2 Immunomodulation of moDCs by Nano-Encapsulated EP2/EP4 Antagonists
- PMID: 36674907
- PMCID: PMC9866164
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24021392
Tailored PGE2 Immunomodulation of moDCs by Nano-Encapsulated EP2/EP4 Antagonists
Abstract
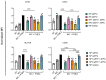
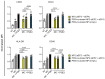
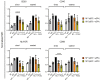
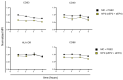
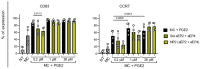
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is an important maturation mediator for dendritic cells (DCs). However, increased PGE2 levels in the tumor exert immunosuppressive effects on DCs by signaling through two E-Prostanoid (EP) receptors: EP2 and EP4. Blocking EP-receptor signaling of PGE2 with antagonists is currently being investigated for clinical applications to enhance anti-tumor immunity. In this study, we investigated a new delivery approach by encapsulating EP2/EP4 antagonists in polymeric nanoparticles. The nanoparticles were characterized for size, antagonist loading, and release. The efficacy of the encapsulated antagonists to block PGE2 signaling was analyzed using monocyte-derived DCs (moDCs). The obtained nanoparticles were sized between 210 and 260 nm. The encapsulation efficacy of the EP2/EP4 antagonists was 20% and 17%, respectively, and was further increased with the co-encapsulation of both antagonists. The treatment of moDCs with co-encapsulation EP2/EP4 antagonists prevented PGE2-induced co-stimulatory marker expression. Even though both antagonists showed a burst release within 15 min at 37 °C, the nanoparticles executed the immunomodulatory effects on moDCs. In summary, we demonstrate the functionality of EP2/EP4 antagonist-loaded nanoparticles to overcome PGE2 modulation of moDCs.
Keywords: EP2/EP4 antagonist; delivery; dendritic cells; nanoparticles; prostaglandin E2.
Conflict of interest statement
J.A.F. is an employee of Miltenyi Biotec B.V. & Co. KG. No competing interest exist for the remaining authors J.B., L.M.K., G.F.-G. and I.J.M.d.V.
Figures
References
-
- Jonuleit H., Kühn U., Müller G., Steinbrink K., Paragnik L., Schmitt E., Knop J., Enk A.H. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins induce maturation of potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells under fetal calf serum-free conditions. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997;27:3135–3142. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830271209. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

