Antiseizure Effects of Scoparone, Borneol and Their Impact on the Anticonvulsant Potency of Four Classic Antiseizure Medications in the Mouse MES Model-An Isobolographic Transformation
- PMID: 36674911
- PMCID: PMC9867083
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24021395
Antiseizure Effects of Scoparone, Borneol and Their Impact on the Anticonvulsant Potency of Four Classic Antiseizure Medications in the Mouse MES Model-An Isobolographic Transformation
Abstract
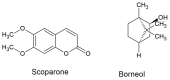
Numerous botanical drugs containing coumarins and terpenes are used in ethnomedicine all over the world for their various therapeutic properties, especially those affecting the CNS system. The treatment of epilepsy is based on antiseizure medications (ASMs), although novel strategies using naturally occurring substances with confirmed antiseizure properties are being developed nowadays. The aim of this study was to determine the anticonvulsant profiles of scoparone (a simple coumarin) and borneol (a bicyclic monoterpenoid) when administered separately and in combination, as well as their impact on the antiseizure effects of four classic ASMs (carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital and valproate) in the mouse model of maximal electroshock-induced (MES) tonic-clonic seizures. MES-induced seizures were evoked in mice receiving the respective doses of the tested natural compounds and classic ASMs (when applied alone or in combinations). Interactions for two-drug and three-drug mixtures were assessed by means of isobolographic transformation of data. Polygonograms were used to illustrate the types of interactions occurring among drugs. The total brain content of ASMs was measured in mice receiving the respective drug treatments with fluorescent polarization immunoassay. Scoparone and borneol, when administered alone, exerted anticonvulsant properties in the mouse MES model. The two-drug mixtures of scoparone with valproate, borneol with phenobarbital and borneol with valproate produced synergistic interactions in the mouse MES model, while the remaining tested two-drug mixtures produced additivity. The three-drug mixtures of scoparone + borneol with valproate and phenobarbital produced synergistic interactions in the mouse MES model. Verification of total brain concentrations of valproate and phenobarbital revealed that borneol elevated the total brain concentrations of both ASMs, while scoparone did not affect the brain content of these ASMs in mice. The synergistic interaction of scoparone with valproate observed in the mouse MES model is pharmacodynamic in nature. Borneol elevated the brain concentrations of the tested ASMs, contributing to the pharmacokinetic nature of the observed synergistic interactions with valproate and phenobarbital in the mouse MES model.
Keywords: antiseizure medication; borneol; coumarin; isobolographic transformation; maximal electroshock; scoparone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Imperatorin interacts additively with novel antiseizure medications in the mouse maximal electroshock-induced seizure model: an isobolographic transformation.Pharmacol Rep. 2024 Feb;76(1):216-222. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00555-4. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Pharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38015370 Free PMC article.
-
Anticonvulsant effects of isopimpinellin and its interactions with classic antiseizure medications and borneol in the mouse tonic-clonic seizure model: an isobolographic transformation.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Dec;75(6):1533-1543. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00532-x. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37821793 Free PMC article.
-
New derivative of 1,2,4-triazole-3-thione (TP427) potentiates the anticonvulsant action of valproate, but not that of carbamazepine, phenytoin or phenobarbital in the mouse tonic-clonic seizure model.Pharmacol Rep. 2019 Apr;71(2):299-305. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2019.01.003. Epub 2019 Jan 6. Pharmacol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30826570
-
Caffeine and Its Interactions with Antiseizure Medications-Is There a Correlation between Preclinical and Clinical Data?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 17;24(24):17569. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417569. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiseizure Medication-Induced Alopecia: A Literature Review.Medicines (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;10(6):35. doi: 10.3390/medicines10060035. Medicines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imperatorin interacts additively with novel antiseizure medications in the mouse maximal electroshock-induced seizure model: an isobolographic transformation.Pharmacol Rep. 2024 Feb;76(1):216-222. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00555-4. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Pharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38015370 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms of Incomptine A in Treating Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Associated with U-937 Cells: Bioinformatics Approaches, Part I.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 24;18(1):5. doi: 10.3390/ph18010005. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39861068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad N., Hui-Yin Y., Makmor-Bakry M. Mechanisms of Natural Products as Potential Antiepileptic Drugs. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022;35:1043–1053. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

