Role of Impaired Glycolysis in Perturbations of Amino Acid Metabolism in Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 36675238
- PMCID: PMC9863464
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24021724
Role of Impaired Glycolysis in Perturbations of Amino Acid Metabolism in Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
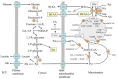
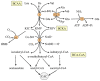
The most frequent alterations in plasma amino acid concentrations in type 1 and type 2 diabetes are decreased L-serine and increased branched-chain amino acid (BCAA; valine, leucine, and isoleucine) levels. The likely cause of L-serine deficiency is decreased synthesis of 3-phosphoglycerate, the main endogenous precursor of L-serine, due to impaired glycolysis. The BCAA levels increase due to decreased supply of pyruvate and oxaloacetate from glycolysis, enhanced supply of NADH + H+ from beta-oxidation, and subsequent decrease in the flux through the citric acid cycle in muscles. These alterations decrease the supply of α-ketoglutarate for BCAA transamination and the activity of branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase, the rate-limiting enzyme in BCAA catabolism. L-serine deficiency contributes to decreased synthesis of phospholipids and increased synthesis of deoxysphinganines, which play a role in diabetic neuropathy, impaired homocysteine disposal, and glycine deficiency. Enhanced BCAA levels contribute to increased levels of aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan), insulin resistance, and accumulation of various metabolites, whose influence on diabetes progression is not clear. It is concluded that amino acid concentrations should be monitored in patients with diabetes, and systematic investigation is needed to examine the effects of L-serine and glycine supplementation on diabetes progression when these amino acids are decreased.
Keywords: branched-chain amino acids; glycine; insulin resistance; serine.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hosseinkhani S., Arjmand B., Dilmaghani-Marand A., Mohammadi Fateh S., Dehghanbanadaki H., Najjar N., Alavi-Moghadam S., Ghodssi-Ghassemabadi R., Nasli-Esfahani E., Farzadfar F., et al. Targeted metabolomics analysis of amino acids and acylcarnitines as risk markers for diabetes by LC-MS/MS technique. Sci. Rep. 2022;12:8418. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11970-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

