Reliability and Validity of Non-Instrumental Clinical Assessments for Adults with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36675650
- PMCID: PMC9861493
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12020721
Reliability and Validity of Non-Instrumental Clinical Assessments for Adults with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
This systematic review on non-instrumental clinical assessment in adult oropharyngeal dysphagia (OD) provides an overview of published measures with reported reliability and validity. In alignment with PRISMA, four databases (CINAHL, Embase, PsycINFO, and PubMed) were searched, resulting in a total of 16 measures and 32 psychometric studies included. The included measures assessed any aspect of swallowing, consisted of at least one specific subscale relating to swallowing, were developed by clinical observation, targeted adults, and were developed in English. The included psychometric studies focused on adults, reported on measures for OD-related conditions, described non-instrumental clinical assessments, reported on validity or reliability, and were published in English. Methodological quality was assessed using the standard quality assessment QualSyst. Most measures targeted only restricted subdomains within the conceptual framework of non-instrumental clinical assessments. Across the 16 measures, hypothesis testing and reliability were the most reported psychometrics, whilst structural validity and content validity were the least reported. Overall, data on the reliability and validity of the included measures proved incomplete and frequently did not meet current psychometric standards. Future research should focus on the development of comprehensive non-instrumental clinical assessments for adults with OD using contemporary psychometric research methods.
Keywords: content validity; deglutition; hypothesis testing; instrument development; internal consistency; measurement; psychometrics; structural validity; swallowing disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
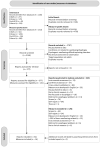
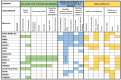
Similar articles
-
Psychometric properties of patient-reported outcome measures for dysphagia in head and neck cancer: a systematic review protocol using COSMIN methodology.Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 15;11(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13643-022-01903-w. Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35168687 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric Characteristics of Non-instrumental Swallowing and Feeding Assessments in Pediatrics: A Systematic Review Using COSMIN.Dysphagia. 2018 Feb;33(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s00455-017-9835-x. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Dysphagia. 2018. PMID: 28819914
-
White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders: Screening and Non-instrumental Assessment for Dysphagia in Adults.Dysphagia. 2022 Apr;37(2):333-349. doi: 10.1007/s00455-021-10283-7. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Dysphagia. 2022. PMID: 33787994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychometric Properties of Visuoperceptual Measures of Videofluoroscopic and Fibre-Endoscopic Evaluations of Swallowing: A Systematic Review.Dysphagia. 2019 Feb;34(1):2-33. doi: 10.1007/s00455-018-9918-3. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Dysphagia. 2019. PMID: 30019178
-
Measuring mealtime performance in older adults with suspected oropharyngeal dysphagia: an updated systematic review of psychometric properties.Disabil Rehabil. 2023 Feb 15:1-15. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2023.2178033. Online ahead of print. Disabil Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 36790118
Cited by
-
Dysphagia and aspiration during a Parkinson's hospitalization: a care partner's perspective and recommendations for improving standards of care.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Oct 9;15:1258979. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1258979. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37876878 Free PMC article.
-
Cranial Nerve Deficits Predict Pharyngeal Phase Swallowing Impairment in Patients with Neurogenic Dysphagia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Dysphagia. 2025 Aug;40(4):886-901. doi: 10.1007/s00455-024-10787-y. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Dysphagia. 2025. PMID: 39652100
-
Esophageal and Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: Clinical Recommendations From the United European Gastroenterology and European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility.United European Gastroenterol J. 2025 Jul;13(6):855-901. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.70062. Epub 2025 Jun 21. United European Gastroenterol J. 2025. PMID: 40543044 Free PMC article.
-
A Psychometric Evaluation of the Dysphagia Handicap Index Using Rasch Analysis.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 17;13(8):2331. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082331. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673604 Free PMC article.
-
Validation and the psychometric properties of the Persian version of the sleep quality scale for coronary care patients: a methodological survey.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 21;15(1):13749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96728-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40258846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Speyer R., Cordier R., Denman D., Windsor C., Krisciunas G.P., Smithard D., Heijnen B.J. Development of Two Patient Self-Reported Measures on Functional Health Status (FOD) and Health-Related Quality of Life (QOD) in Adults with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia Using the Delphi Technique. J. Clin. Med. 2022;11:5920. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195920. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

