The Urine Calcium/Creatinine Ratio and Uricemia during Hyponatremia of Different Origins: Clinical Implications
- PMID: 36675652
- PMCID: PMC9863532
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12020723
The Urine Calcium/Creatinine Ratio and Uricemia during Hyponatremia of Different Origins: Clinical Implications
Abstract
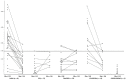
Background: Chronic hyponatremia is known to be associated with osteoporosis. It has been shown that chronic hyponatremia increases bone resorption in an attempt to release body stores of exchangeable sodium by different mechanisms. We wanted to know the calciuria of patients with hyponatremia of different origins. Material and Methods: We made a retrospective study of 114 consecutive patients with asymptomatic hyponatremia of different origins with the usual serum and urine chemistry. Result: In hyponatremia due to SIADH, we had a high urine calcium/creatinine ratio of 0.23 ± 0.096 while in patients with salt depletion the UCa/UCr ratio was low (0.056 ± 0.038), in patients with hyponatremia secondary to thiazide intake the value was also low (0.075 ± 0.047) as in hypervolemic patients (0.034 ± 0.01). In hyponatremia due to polydipsia, the value was high (0.205 ± 0.10). Correction of hyponatremia in the euvolemic patients was associated with a significant decrease in the UCa/UCr ratio. In patients with hyponatremia secondary to thiazide intake, we noted that in the patients with low uric acid levels (<4 mg/dL, suggesting euvolemia) we also observed a low UCa/UCr (<0.10). In nine patients with chronic SIADH (SNa 125.1 ± 3.6 mEq/L), the 24 h urine calcium excretion was 275 ± 112 mg and decreased to 122 ± 77 mg (p < 0.01) after at least 2 weeks of treatment. Conclusions: Patients with chronic hyponatremia due to SIADH usually have a high UCa/UCr ratio (>0.15). This is also observed in hyponatremia secondary to polydipsia. Patients with thiazide-induced hyponatremia usually have low UCa/UCr levels and this is the case even among those with a biochemistry similar to that in SIADH (uric acid < 4 mg/dL).
Keywords: SIADH; calciuria; hyponatremia; polydipsia; thiazides; uricemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tamma R., Sun L., Cuscito C., Lu P., Corcelli M., Li J., Colaianni G., Moonga S.S., Di Benedetto A., Grano M., et al. Regulation of bone remodeling by vasopressin explains the bone loss in hyponatremia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:18644–18649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1318257110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials