Cytokines and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Biomarkers of a Deadly Embrace
- PMID: 36675666
- PMCID: PMC9865677
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13010005
Cytokines and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Biomarkers of a Deadly Embrace
Abstract
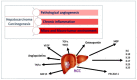
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents a worldwide health matter with a major care burden, high prevalence, and poor prognosis. Its pathogenesis mainly varies depending on the underlying etiological factors, although it develops from liver cirrhosis in the majority of cases. This review summarizes the role of the most interesting soluble factors as biomarkers for early diagnosis and as recommended targets for treatment in accordance with the new challenges in precision medicine. In the premalignant environment, inflammatory cells release a wide range of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, prostaglandins, and proangiogenic factors, making the liver environment more suitable for hepatocyte tumor progression that starts from acquired genetic mutations. A complex interaction of pro-inflammatory (IL-6, TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory cytokines (TGF-α and -β), pro-angiogenic molecules (including the Angiopoietins, HGF, PECAM-1, HIF-1α, VEGF), different transcription factors (NF-kB, STAT-3), and their signaling pathways are involved in the development of HCC. Since cytokines are expressed and released during the different stages of HCC progression, their measurement, by different available methods, can provide in-depth information on the identification and management of HCC.
Keywords: biomarkers; cytokines; hepatocellular carcinoma; personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- AIOM. AIRTUM I Numeri Del Cancro in Italia, XI Edizione 2021. [(accessed on 1 January 2021)]. Available online: https://www.aiom.it/i-numeri-del-cancro-in-italia/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

