FairEmbo Concept for Postpartum Hemorrhage: Evaluation of the Efficacy of Suture Fragment Compared with Gelatin Sponge Torpedo Embolization in a Post-Gravid Swine Model
- PMID: 36675785
- PMCID: PMC9866904
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13010124
FairEmbo Concept for Postpartum Hemorrhage: Evaluation of the Efficacy of Suture Fragment Compared with Gelatin Sponge Torpedo Embolization in a Post-Gravid Swine Model
Abstract
Background: Postpartum hemorrhage is the leading cause of maternal mortality in emerging countries. This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of uterine artery embolization (UAE) using suture fragment (FairEmbo concept) in a swine model.
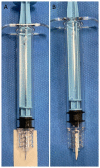
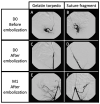
Methods: Seven female swine uteri were embolized. The left uterine artery was embolized with 1 cm fragments of absorbable suture (Optime® 0), and with gelatin sponge torpedoes for the contralateral side for comparison. The embolization effectiveness and the time for arterial recanalization with digital subtraction angiography (DSA) controls at D0, D7, and M1, were evaluated. Follow-up protocol also included clinical monitoring and macroscopical analyses at M1. A Mann-Whitney test (significance at P 0.05) was used for statistics.
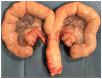
Results: A technical success was obtained for the seven arteries on each side, with no off-target embolization. The procedure time (10 min versus 3.7 min) and number of fragments (13.8 versus 5.7) required for complete occlusion were significantly greater in the FairEmbo group. All arteries were repermeabilized at M1. No necrosis was macroscopically visible at harvest at M1.
Conclusion: This experimental study suggests that UAE with SBM FairEmbo method is feasible, safe, and effective in comparison with gelatin sponge procedure.
Keywords: FairEmbo; gelatin sponge; postpartum hemorrhage; suture; uterine artery embolization (UAE).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FairEmbo Concept for Arterial Embolizations: In Vivo Feasibility and Safety Study with Suture-Based Microparticles Compared with Microspheres.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021 Apr;44(4):625-632. doi: 10.1007/s00270-020-02678-0. Epub 2020 Oct 25. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33099701
-
Comparison of Uterine Necrosis After Uterine Artery Embolization with Soluble Gelatin Sponge Particles or Tris-acryl Gelatin Microspheres in Swine.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021 Nov;44(11):1780-1789. doi: 10.1007/s00270-021-02905-2. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34231005
-
In Vivo Feasibility of Arterial Embolization with Permanent and Absorbable Suture: The FAIR-Embo Concept.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019 Aug;42(8):1175-1182. doi: 10.1007/s00270-019-02211-y. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31025052
-
Successful repeated uterine artery embolization in postpartum hemorrhage with disseminated intravascular coagulation: a case report and literature review.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021 Oct 22;21(1):710. doi: 10.1186/s12884-021-04191-9. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021. PMID: 34686156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of arterial embolization in the management of postpartum hemorrhage].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2014 Dec;43(10):1063-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Nov 7. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2014. PMID: 25447393 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Feasibility of the FairEmbo Concept to Treat Women Postpartum Hemorrhage: Embolization with Suture Fragments.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024 Apr;47(4):520-523. doi: 10.1007/s00270-023-03626-4. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38112752 No abstract available.
-
Sequential Aspiration and injection of a Mixture of gelatin-based hemostatic agent and autologous blood clot followed by suture coiling for Effective Embolization of splenic artery pseudoaneurysm by interventional Radiologist (SAMEER): Description of a novel technique.Radiol Case Rep. 2025 Mar 29;20(6):3024-3030. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2025.03.006. eCollection 2025 Jun. Radiol Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40230714 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

