Type 2C Protein Phosphatases MoPtc5 and MoPtc7 Are Crucial for Multiple Stress Tolerance, Conidiogenesis and Pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae
- PMID: 36675822
- PMCID: PMC9863299
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9010001
Type 2C Protein Phosphatases MoPtc5 and MoPtc7 Are Crucial for Multiple Stress Tolerance, Conidiogenesis and Pathogenesis of Magnaporthe oryzae
Abstract
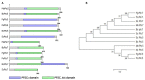
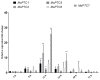
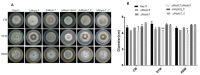
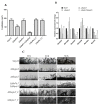
Protein kinases and phosphatases catalyze the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of their protein substrates, respectively, and these are important mechanisms in cellular signal transduction. The rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae possesses 6 protein phosphatases of type 2C class, including MoPtc1, 2, 5, 6, 7 and 8. However, only very little is known about the roles of these phosphatases in filamentous fungi. Here in, we deployed genetics and molecular biology techniques to identify, characterize and establish the roles of MoPtc5 and MoPtc7 in M. oryzae development and pathogenicity. We found that during pathogen-host interaction, MoPTC7 is differentially expressed. Double deletion of MoPTC7 and MoPTC5 suppressed the fungal vegetative growth, altered its cell wall integrity and reduced its virulence. The two genes were found indispensable for stress tolerance in the phytopathogen. We also demonstrated that disruption of any of the two genes highly affected appressorium turgor generation and Mps1 and Osm1 phosphorylation levels. Lastly, we demonstrated that both MoPtc5 and MoPtc7 are localized to mitochondria of different cellular compartments in the blast fungus. Taken together, our study revealed synergistic coordination of M. oryzae development and pathogenesis by the type 2C protein phosphatases.
Keywords: blast fungus; pathogenicity; phosphorylation; protein phosphatases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirmed no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein Phosphatases MoPtc5, MoPtc1, and MoPtc2 Contribute to the Vegetative Growth, Stress Adaptation, and Virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;11(3):231. doi: 10.3390/jof11030231. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137268 Free PMC article.
-
The Calcium Chloride Responsive Type 2C Protein Phosphatases Play Synergistic Roles in Regulating MAPK Pathways in Magnaporthe oryzae.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Dec 8;8(12):1287. doi: 10.3390/jof8121287. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36547620 Free PMC article.
-
eIF3k Domain-Containing Protein Regulates Conidiogenesis, Appressorium Turgor, Virulence, Stress Tolerance, and Physiological and Pathogenic Development of Magnaporthe oryzae Oryzae.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 18;12:748120. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.748120. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34733303 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the cell and developmental biology of plant infection by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.Fungal Genet Biol. 2021 Sep;154:103562. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2021.103562. Epub 2021 Apr 18. Fungal Genet Biol. 2021. PMID: 33882359 Review.
-
The role of glycerol in the pathogenic lifestyle of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.Environ Microbiol. 2017 Mar;19(3):1008-1016. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13688. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28165657 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterisation of guided entry of tail-anchored proteins in Magnaporthe oryzae.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jul 28;21(7):e1013011. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013011. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40720549 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Phosphatases MoPtc5, MoPtc1, and MoPtc2 Contribute to the Vegetative Growth, Stress Adaptation, and Virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;11(3):231. doi: 10.3390/jof11030231. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137268 Free PMC article.
-
Type 2C Protein Phosphatase MoPtc6 Plays Critical Roles in the Development and Virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 Apr 24;11(5):335. doi: 10.3390/jof11050335. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422669 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

