Expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RER2 Gene Encoding Cis-Prenyltransferase in Trichoderma atroviride Increases the Activity of Secretory Hydrolases and Enhances Antimicrobial Features
- PMID: 36675859
- PMCID: PMC9860738
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9010038
Expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RER2 Gene Encoding Cis-Prenyltransferase in Trichoderma atroviride Increases the Activity of Secretory Hydrolases and Enhances Antimicrobial Features
Abstract
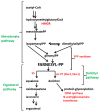
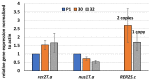
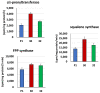
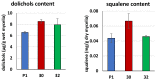
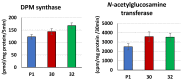
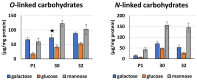
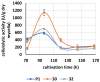
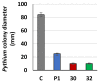
Some Trichoderma spp. exhibit natural abilities to reduce fungal diseases of plants through their mycoparasitic and antagonistic properties. In this study, we created new Trichoderma atroviride strains with elevated antifungal activity. This effect was achieved by improving the activity of cis-prenyltransferase, the main enzyme in dolichol synthesis, by expressing the RER2 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Since dolichyl phosphate is the carrier of carbohydrate residues during protein glycosylation, activation of its synthesis enhanced the activities of dolichyl-dependent enzymes, DPM synthase and N-acetylglucosamine transferase, as well as stimulated glycosylation of secretory proteins. Cellulases secreted by the transformants revealed significantly higher levels or activities compared to the control strain. Consequently, the resulting Trichoderma strains were more effective against the plant pathogens Pythium ultimum.
Keywords: T. atroviride; antimicrobial activity; cis-prenyltransferase; glycosylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased activity of the sterol branch of the mevalonate pathway elevates glycosylation of secretory proteins and improves antifungal properties of Trichoderma atroviride.Fungal Genet Biol. 2020 Apr;137:103334. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2020.103334. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Fungal Genet Biol. 2020. PMID: 31958566
-
Elevated activity of dolichyl phosphate mannose synthase enhances biocontrol abilities of Trichoderma atroviride.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011 Dec;24(12):1522-9. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-11-0025. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011. PMID: 21770768
-
Overexpression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RER2 gene in Trichoderma reesei affects dolichol dependent enzymes and protein glycosylation.Fungal Genet Biol. 2006 Jun;43(6):422-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2006.01.009. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Fungal Genet Biol. 2006. PMID: 16527501
-
Protein glycosylation in pmt mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Influence of heterologously expressed cellobiohydrolase II of Trichoderma reesei and elevated levels of GDP-mannose and cis-prenyltransferase activity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 May;1770(5):774-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.01.010. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17343985
-
Modulation of mannosylphosphodolichol synthase and dolichol kinase activity in Trichoderma, related to protein secretion.Acta Biochim Pol. 1994;41(3):331-7. Acta Biochim Pol. 1994. PMID: 7856404 Review.
References
-
- Benitez T., Rincon A.M., Limon M.C., Codon A.C. Biocontrol mechanisms of Trichoderma strains. Internat. Microbiol. 2004;7:249–260. - PubMed
-
- Palamarczyk G., Maras M., Contreras R., Kruszewska J. Protein secretion and glycosylation in Trichoderma. In: Kubicek C.P., Harman G.E., editors. Trichoderma and Glocladium. Volume 1. Taylor and Francis Ltd.; London, UK: 1998. pp. 121–138.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

