Impact of Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus on Breakthrough Mucormycosis Outcomes in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies-Complex and Intriguing Associations
- PMID: 36675866
- PMCID: PMC9860539
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9010045
Impact of Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus on Breakthrough Mucormycosis Outcomes in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies-Complex and Intriguing Associations
Abstract
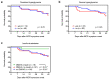
Mucormycosis (MCR) is frequently associated with diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemia, as well as hematologic malignancies (HMs) and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). However, little is known about the effect of hyperglycemia on MCR outcomes in patients with HMs. We therefore conducted a retrospective cohort study of adult patients hospitalized with MCR and HM or HSCT (n = 103) at MD Anderson Cancer Center from April 2000 through to April 2020. Twenty-three patients (22%) had documented episodes of severe hyperglycemia. Sixty patients had >5 serum glucose measurements within 28 days prior to MCR symptom onset; of those, 14 (23%) met the criteria for persistent hyperglycemia. Sixteen patients (16%) received insulin prior to admission. The crude mortality 42 days from the onset of MCR symptoms in our cohort was 31%. Neither severe nor persistent hyperglycemia were associated with excess mortality. Insulin use prior to index admission was associated with decreased 42-day mortality on univariate analysis (p = 0.031). In conclusion, in a setting of high crude mortality, severe and/or persistent hyperglycemia do not appear to be associated with excess mortality in patients with HM or HSCT developing MCR. Insulin use prior to MCR diagnosis may be associated with decreased mortality, although further research is needed to validate this effect and to study its mechanistic underpinnings.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; hematologic malignancy; hyperglycemia; insulin; mortality; mucormycosis.
Conflict of interest statement
D.P.K. reports honoraria and research support from Gilead Sciences and Astellas, Inc., received consultant fees from Astellas Pharma, Merck, and Gilead Sciences, and is a member of the Data Review Committee of Cidara Therapeutics, AbbVie, and the Mycoses Study Group. All other authors report no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Breakthrough Mucormycosis Developing on Mucorales-Active Antifungals Portrays a Poor Prognosis in Patients with Hematologic Cancer.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Mar 17;7(3):217. doi: 10.3390/jof7030217. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802827 Free PMC article.
-
Report of the Committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002 Jan;55(1):65-85. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8227(01)00365-5. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002. PMID: 11755481
-
Initial use of combination treatment does not impact survival of 106 patients with haematologic malignancies and mucormycosis: a propensity score analysis.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016 Sep;22(9):811.e1-811.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.03.029. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016. PMID: 27085727
-
Clinical Manifestations of Pulmonary Mucormycosis in Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A 21-Case Series Report and Literature Review.Can Respir J. 2022 Jun 2;2022:1237125. doi: 10.1155/2022/1237125. eCollection 2022. Can Respir J. 2022. PMID: 35692949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal Infections of the Stem Cell Transplant Recipient and Hematologic Malignancy Patients.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;33(2):545-566. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2019.02.006. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 31005138 Review.
Cited by
-
Siderophore-synthesizing NRPS reprogram lipid metabolic profiles for phenotype and function changes of Arthrobotrys oligospora.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 20;40(2):46. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03840-9. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38114752
-
The Impact of Dimitrios P. Kontoyiannis on Mucormycosis Research.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 May 27;10(6):382. doi: 10.3390/jof10060382. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921367 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

