The ERAD Pathway Participates in Fungal Growth and Cellulase Secretion in Trichoderma reesei
- PMID: 36675895
- PMCID: PMC9862206
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9010074
The ERAD Pathway Participates in Fungal Growth and Cellulase Secretion in Trichoderma reesei
Abstract
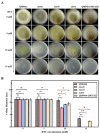
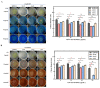
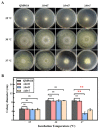
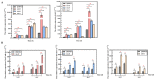
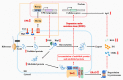
Trichoderma reesei is a powerful fungal cell factory for the production of cellulolytic enzymes due to its outstanding protein secretion capacity. Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) plays an integral role in protein secretion that responds to secretion pressure and removes misfolded proteins. However, the role of ERAD in fungal growth and endogenous protein secretion, particularly cellulase secretion, remains poorly understood in T. reesei. Here, we investigated the ability of T. reesei to grow under different stresses and to secrete cellulases by disrupting three major genes (hrd1, hrd3 and der1) involved in the critical parts of the ERAD pathway. Under the ER stress induced by high concentrations of DTT, knockout of hrd1, hrd3 and der1 resulted in severely impaired growth, and the mutants Δhrd1 and Δhrd3 exhibited high sensitivity to the cell wall-disturbing agents, CFW and CR. In addition, the absence of either hrd3 or der1 led to the decreased heat tolerance of this fungus. These mutants showed significant differences in the secretion of cellulases compared to the parental strain QM9414. During fermentation, the secretion of endoglucanase in the mutants was essentially consistent with that of the parental strain, while cellobiohydrolase and β-glucosidase were declined. It was further discovered that the transcription levels of the endoglucanase-encoding genes (eg1 and eg2) and the cellobiohydrolase-encoding gene (cbh1) were not remarkedly changed. However, the β-glucosidase-encoding gene (bgl1) was significantly downregulated in the ERAD-deficient mutants, which was presumably due to the activation of a proposed feedback mechanism, repression under secretion stress (RESS). Taken together, our results indicate that a defective ERAD pathway negatively affects fungal growth and cellulase secretion, which provides a novel insight into the cellulase secretion mechanism in T. reesei.
Keywords: ERAD; Trichoderma reesei; cellulase secretion; endoplasmic reticulum stress; fungal growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Liu G., Qu Y. Integrated engineering of enzymes and microorganisms for improving the efficiency of industrial lignocellulose deconstruction. Eng. Microbiol. 2021;1:100005. doi: 10.1016/j.engmic.2021.100005. - DOI
-
- Xue X., Wu Y., Qin X., Ma R., Luo H., Su X., Yao B. Revisiting overexpression of a heterologous β-glucosidase in Trichoderma reesei: Fusion expression of the Neosartorya fischeri Bgl3A to cbh1 enhances the overall as well as individual cellulase activities. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016;15:122. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0520-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

