Insights into the Genomic and Phenotypic Landscape of the Oleaginous Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica
- PMID: 36675897
- PMCID: PMC9865632
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9010076
Insights into the Genomic and Phenotypic Landscape of the Oleaginous Yeast Yarrowia lipolytica
Abstract
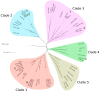
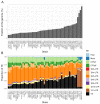
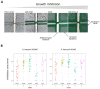
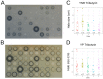
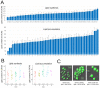
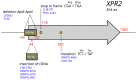
Although Yarrowia lipolytica is a model yeast for the study of lipid metabolism, its diversity is poorly known, as studies generally consider only a few standard laboratory strains. To extend our knowledge of this biotechnological workhorse, we investigated the genomic and phenotypic diversity of 56 natural isolates. Y. lipolytica is classified into five clades with no correlation between clade membership and geographic or ecological origin. A low genetic diversity (π = 0.0017) and a pan-genome (6528 genes) barely different from the core genome (6315 genes) suggest Y. lipolytica is a recently evolving species. Large segmental duplications were detected, totaling 892 genes. With three new LTR-retrotransposons of the Gypsy family (Tyl4, Tyl9, and Tyl10), the transposable element content of genomes appeared diversified but still low (from 0.36% to 3.62%). We quantified 34 traits with substantial phenotypic diversity, but genome-wide association studies failed to evidence any associations. Instead, we investigated known genes and found four mutational events leading to XPR2 protease inactivation. Regarding lipid metabolism, most high-impact mutations were found in family-belonging genes, such as ALK or LIP, and therefore had a low phenotypic impact, suggesting that the huge diversity of lipid synthesis and accumulation is multifactorial or due to complex regulations.
Keywords: diversity; killer toxin; phenotype; population genomics; transposable elements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring Proteomes of Robust Yarrowia lipolytica Isolates Cultivated in Biomass Hydrolysate Reveals Key Processes Impacting Mixed Sugar Utilization, Lipid Accumulation, and Degradation.mSystems. 2021 Aug 31;6(4):e0044321. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00443-21. Epub 2021 Aug 3. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34342539 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of yeast from the Yarrowia clade for lipid production in dilute acid pretreated lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysate.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Apr;101(8):3319-3334. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-8062-y. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28012044
-
Sequence Assembly of Yarrowia lipolytica Strain W29/CLIB89 Shows Transposable Element Diversity.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 7;11(9):e0162363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162363. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27603307 Free PMC article.
-
Yarrowia lipolytica Strains and Their Biotechnological Applications: How Natural Biodiversity and Metabolic Engineering Could Contribute to Cell Factories Improvement.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Jul 10;7(7):548. doi: 10.3390/jof7070548. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering Yarrowia lipolytica for Use in Biotechnological Applications: A Review of Major Achievements and Recent Innovations.Mol Biotechnol. 2018 Aug;60(8):621-635. doi: 10.1007/s12033-018-0093-4. Mol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29943148 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the genomic and phenotypic diversity of Monosporozyma unispora strains isolated from anthropic environments.FEMS Yeast Res. 2025 Jan 30;25:foaf016. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foaf016. FEMS Yeast Res. 2025. PMID: 40121180 Free PMC article.
-
Advances and perspectives in genetic expression and operation for the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 May 10;9(4):618-626. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.05.003. eCollection 2024 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38784195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

