First-Trimester Maternal Serum Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio in Pre-Eclampsia and Fetal Growth
- PMID: 36676079
- PMCID: PMC9864486
- DOI: 10.3390/life13010130
First-Trimester Maternal Serum Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio in Pre-Eclampsia and Fetal Growth
Abstract
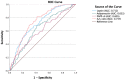
The serum adiponectin/leptin ratio (A/L ratio) is a surrogate marker of insulin sensitivity. Pre-eclampsia (PE) is associated with maternal metabolic syndrome and occasionally impaired fetal growth. We assessed whether the A/L ratio in first-trimester maternal serum was associated with PE and/or birth weight. Adiponectin and leptin were quantitated in first-trimester blood samples (gestational week 10+3−13+6) from 126 women who later developed PE with proteinuria (98 mild PE; 21 severe PE; 7 HELLP syndrome), and 297 controls, recruited from the Copenhagen First-Trimester Screening Study. The A/L ratio was reduced in PE pregnancies, median 0.17 (IQR: 0.12−0.27) compared with controls, median 0.32 (IQR: 0.19−0.62) (p < 0.001). A multiple logistic regression showed that PE was negatively associated with log A/L ratio independent of maternal BMI (odds ratio = 0.315, 95% CI = 0.191 to 0.519). Adiponectin (AUC = 0.632) and PAPP-A (AUC = 0.605) were negatively associated with PE, and leptin (AUC = 0.712) was positively associated with PE. However, the A/L ratio was a better predictor of PE (AUC = 0.737), albeit not clinically relevant as a single marker. No significant association was found between A/L ratio and clinical severity of pre-eclampsia or preterm birth. PE was associated with a significantly lower relative birth weight (p < 0.001). A significant negative correlation was found between relative birth weight and A/L ratio in controls (β = −0.165, p < 0.05) but not in PE pregnancies), independent of maternal BMI. After correction for maternal BMI, leptin was significantly associated with relative birth weight (β = 2.98, p < 0.05), while adiponectin was not significantly associated. Our findings suggest that an impairment of the A/L ratio (as seen in metabolic syndrome) in the first trimester is characteristic of PE, while aberrant fetal growth in PE is not dependent on insulin sensitivity, but rather on leptin-associated pathways.
Keywords: A/L ratio; adipocytokine; adiponectin; birth weight; leptin; metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Recommendations for Prevention and Treatment of Pre-Eclampsia and Eclampsia. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011. [(accessed on 3 June 2020)]. (WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee) Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK140561/ - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Ventura V., Li Y., Pasupuleti V., Roman Y.M., Hernandez A.V., Pérez-López F.R. Effects of preeclampsia and eclampsia on maternal metabolic and biochemical outcomes in later life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2019;102:154012. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

