Curcumin in Wound Healing-A Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 36676091
- PMCID: PMC9866018
- DOI: 10.3390/life13010143
Curcumin in Wound Healing-A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
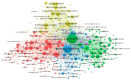
Background: Curcumin has been widely used to treat a variety of diseases and disorders since ancient times, most notably for the purpose of healing wounds. Despite the large number of available reviews on this topic, a bibliometric tool-based meta-analysis is missing in the literature. Scope and approach: To evaluate the influence and significance of the countries, journals, organizations and authors that have contributed the most to this topic, the popular bibliometric markers, including article count, citation count, and Hirsch index (H-index), are taken into account. Their collaborative networks and keyword co-occurrence along with the trend analysis are also sketched out using the VOSviewer software. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first bibliometric review on the topic and hence it is envisaged that it will attract researchers to explore future research dimensions in the related field.
Key findings and conclusions: India provided the most articles, making up more than 27.49 percent of the entire corpus. The International Journal of Biological Macromolecules published the most articles (44), and it also received the most citations (2012). The Journal of Ethnopharmacology (28 articles) and Current Pharmaceutical Design (20 articles) were the next most prolific journals with 1231 and 812 citations, respectively. The results indicate a significant increase in both research and publications on the wound-healing properties of curcumin. Recent studies have concentrated on creating novel medicine-delivery systems that use nano-curcumin to boost the effect of the curcumin molecule in therapeutic targeting. It has also been observed that genetic engineering and biotechnology have recently been employed to address the commercial implications of curcumin.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; curcuma longa; curcumin; turmeric; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Bhandari P.R. Garlic (Allium sativum L.): A review of potential therapeutic applications. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2012;6:118–129. doi: 10.4103/0973-8258.102826. - DOI
-
- Khushbu C., Roshni S., Anar P., Carol M., Mayuree P. Phytochemical and therapeutic potential of Piper longum Linn a review. Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 2011;2:157–161.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

