ECMO Retrieval Program: What Have We Learned So Far
- PMID: 36676106
- PMCID: PMC9865097
- DOI: 10.3390/life13010157
ECMO Retrieval Program: What Have We Learned So Far
Abstract
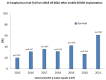
Veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) is increasingly used for patients with cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. However, survival rates remain low. It is unclear to what extent ECMO patients benefit from the ECMO team learning curve. Therefore, we aimed to analyze our mobile ECMO program patients from the past seven years to evaluate if a learning curve benefits patients’ outcomes. We analyzed 111 patients from our databank who were supported with a VA-ECMO and brought to our hospital from January 2015 to December 2021. Patients were divided into two groups: survival (n = 70) and non-survival (n = 41). As expected, complications after ECMO implantation were more severe in the non-survivor group. The incidence of thromboembolic events (p = 0.002), hepatic failure (p < 0.001), renal failure (p = 0.002), dialysis (p = 0.002) and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS, p = 0.044) occurred significantly more often compared with the survivor group. We were able to show that despite our extensive experience in terms of ECMO retrieval program the high mortality and morbidity rates stay fairly the same over the years. This displays that we have to focus even more on patient selection and ECMO indication.
Keywords: ECMO; cardiogenic shock; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lunz D., Calabrò L., Belliato M., Contri E., Broman L.M., Scandroglio A.M., Patricio D., Malfertheiner M., Creteur J., Philipp A., et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for refractory cardiac arrest: A retrospective multicenter study. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46:973–982. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-05926-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ostadal P., Rokyta R., Kruger A., Vondrakova D., Janotka M., Smíd O., Smalcova J., Hromadka M., Linhart A., Bělohlávek J. Extra corporeal membrane oxygenation in the therapy of cardiogenic shock (ECMO-CS): Rationale and design of the multicenter randomized trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017;19((Suppl. 2)):124–127. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.857. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carroll B.J., Shah R.V., Murthy V., McCullough S.A., Reza N., Thomas S.S., Song T.H., Newton-Cheh C.H., Camuso J.M., MacGillivray T., et al. Clinical Features and outcomes in adults with cardiogenic shock supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015;116:1624–1630. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.08.030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lorusso R., Shekar K., MacLaren G., Schmidt M., Pellegrino V., Meyns B., Haft J., Vercaemst L., Pappalardo F., Bermudez C., et al. ELSO Interim Guidelines for Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Adult Cardiac Patients. Asaio J. 2021;67:827–844. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001510. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kaushal M., Schwartz J., Gupta N., Im J., Leff J., Jakobleff W.A., Leyvi G. Patient Demographics and Extracorporeal Membranous Oxygenation (ECMO)-Related Complications Associated With Survival to Discharge or 30-Day Survival in Adult Patients Receiving Venoarterial (VA) and Venovenous (VV) ECMO in a Quaternary Care Urban Center. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019;33:910–917. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2018.08.193. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous