A Prospective Approach to Integration of AI Fracture Detection Software in Radiographs into Clinical Workflow
- PMID: 36676172
- PMCID: PMC9864518
- DOI: 10.3390/life13010223
A Prospective Approach to Integration of AI Fracture Detection Software in Radiographs into Clinical Workflow
Abstract
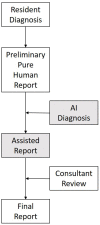
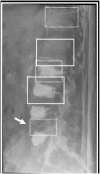
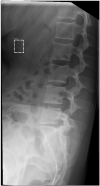
Gleamer BoneView© is a commercially available AI algorithm for fracture detection in radiographs. We aim to test if the algorithm can assist in better sensitivity and specificity for fracture detection by residents with prospective integration into clinical workflow. Radiographs with inquiry for fracture initially reviewed by two residents were randomly assigned and included. A preliminary diagnosis of a possible fracture was made. Thereafter, the AI decision on presence and location of possible fractures was shown and changes to diagnosis could be made. Final diagnosis of fracture was made by a board-certified radiologist with over eight years of experience, or if available, cross-sectional imaging. Sensitivity and specificity of the human report, AI diagnosis, and assisted report were calculated in comparison to the final expert diagnosis. 1163 exams in 735 patients were included, with a total of 367 fractures (31.56%). Pure human sensitivity was 84.74%, and AI sensitivity was 86.92%. Thirty-five changes were made after showing AI results, 33 of which resulted in the correct diagnosis, resulting in 25 additionally found fractures. This resulted in a sensitivity of 91.28% for the assisted report. Specificity was 97.11, 84.67, and 97.36%, respectively. AI assistance showed an increase in sensitivity for both residents, without a loss of specificity.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; computer-aided diagnosis; fracture; radiographs.
Conflict of interest statement
Stefan Niehues has received research grants from Bracco Group, Bayer Vital GmbH, Canon Medical Systems, and Guerbet. Bernd Hamm has received research grants for the Department of Radiology, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin from the following companies: (1) Abbott, (2) Actelion Pharmaceuticals, (3) Bayer Schering Pharma, (4) Bayer Vital, (5) BRACCO Group, (6) Bristol-Myers Squibb, (7) Charite Research Organisation GmbH, (8) Deutsche Krebshilfe, (9) Dt. Stiftung für Herzforschung, (10) Essex Pharma, (11) EU Programmes, (12) FibrexMedical Inc, (13) Focused Ultrasound Surgery Foundation, (14) Fraunhofer Gesellschaft, (15) Guerbet, (16) INC Research, (17) lnSightec Ud, (18) IPSEN Pharma, (19) Kendlel MorphoSys AG, (20) Lilly GmbH, (21) Lundbeck GmbH, (22) MeVis Medical Solutions AG, (23) Nexus Oncology, (24) Novartis, (25) Parexel Clinical Research Organisation Service, (26) Perceptive, (27) Pfizer GmbH, (28) Philipps, (29) Sanofis-Aventis S.A., (30) Siemens, (31) Spectranetics GmbH, (32) Terumo Medical Corporation, (33) TNS Healthcare GMbH, (34) Toshiba, (35) UCB Pharma, (36) Wyeth Pharma, (37) Zukunftsfond Berlin (TSB), (38) Amgen, (39) AO Foundation, (40) BARD, (41) BBraun, (42) Boehring Ingelheimer, (43) Brainsgate, (44) PPD (Clinical Research Organisation), (45) CELLACT Pharma, (46) Celgene, (47) CeloNova Bio-Sciences, (48) Covance, (49) DC Deviees, Ine. USA, (50) Ganymed, (51) Gilead Sciences, (52) GlaxoSmithKline, (53) ICON (Clinical Research Organisation), (54) Jansen, (55) LUX Bioseienees, (56) MedPass, (57) Merek, (58) Mologen, (59) Nuvisan, (60) Pluristem, (61) Quintiles, (62) Roehe, (63) SehumaeherGmbH (Sponsoring eines Workshops), (64) Seattle Geneties, (65) Symphogen, (66) TauRx Therapeuties Ud, (67) Accovion, (68) AIO: Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie, (69) ASR Advanced sleep research, (70) Astellas, (71) Theradex, (72) Galena Biopharma, (73) Chiltern, (74) PRAint, (75) lnspiremd, (76) Medronic, (77) Respicardia, (78) Silena Therapeutics, (79) Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, (80) St Jude, (81) TEVA, (82) Theorem, (83) Abbvie, (84) Aesculap, (85) Biotronik, (86) Inventivhealth, (87) ISATherapeutics, (88) LYSARC, (89) MSD, (90) Novocure, (91) Ockham Oncology, (92) Premier-Research, (93) Psi-cro, (94) Tetec-ag, (95) Winicker-Norimed, (96) Achaogen Inc, (97) ADIR, (98) AstraZenaca AB, (99) Demira Inc, (100) Euroscreen S.A., (101) Galmed Research and Development Ltd., (102) GETNE, (103) Guidant Europe NV, (104) Holaira Inc, (105) Immunomedics Inc, (106) Innate Pharma, (107) Isis Pharmaceuticals Inc, (108) Kantar Health GmbH, (109) MedImmune Inc, (110) Medpace Germany GmbH (CRO), (111) Merrimack Pharmaceuticals Inc, (112) Millenium Pharmaceuticals Inc, (113) Orion Corporation Orion Pharma, (114) Pharmacyclics Inc, (115) PIQUR Therapeutics Ltd., (116) Pulmonx International Sárl, (117) Servier (CRO), (118) SGS Life Science Services (CRO), and (119) Treshold Pharmaceuticals Inc. These grants had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest and did not receive any funds.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence and pelvic fracture diagnosis on X-rays: a preliminary study on performance, workflow integration and radiologists' feedback assessment in a spoke emergency hospital.Eur J Radiol Open. 2023 Jul 6;11:100504. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100504. eCollection 2023 Dec. Eur J Radiol Open. 2023. PMID: 37484978 Free PMC article.
-
Real-life benefit of artificial intelligence-based fracture detection in a pediatric emergency department.Eur Radiol. 2025 Apr 7. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11554-9. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40192806
-
Artificial Intelligence for Detecting Acute Fractures in Patients Admitted to an Emergency Department: Real-Life Performance of Three Commercial Algorithms.Acad Radiol. 2023 Oct;30(10):2118-2139. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.06.016. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Acad Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37468377
-
What Are the Applications and Limitations of Artificial Intelligence for Fracture Detection and Classification in Orthopaedic Trauma Imaging? A Systematic Review.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Nov;477(11):2482-2491. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000848. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 31283727 Free PMC article.
-
Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of subepithelial lesions using endoscopic ultrasonography: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 15;12:915481. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.915481. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36046054 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence and pelvic fracture diagnosis on X-rays: a preliminary study on performance, workflow integration and radiologists' feedback assessment in a spoke emergency hospital.Eur J Radiol Open. 2023 Jul 6;11:100504. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100504. eCollection 2023 Dec. Eur J Radiol Open. 2023. PMID: 37484978 Free PMC article.
-
Added value of artificial intelligence for the detection of pelvic and hip fractures.Jpn J Radiol. 2025 Jul;43(7):1166-1175. doi: 10.1007/s11604-025-01754-0. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Jpn J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40038216
-
Improving traumatic fracture detection on radiographs with artificial intelligence support: a multi-reader study.BJR Open. 2024 Apr 25;6(1):tzae011. doi: 10.1093/bjro/tzae011. eCollection 2024 Jan. BJR Open. 2024. PMID: 38757067 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Spine Surgery: Imaging-Based Applications for Diagnosis and Surgical Techniques.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2025 Oct;18(10):398-405. doi: 10.1007/s12178-025-09972-9. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2025. PMID: 40304942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Identification and Evaluation of Bone Fractures.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Mar 29;11(4):338. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11040338. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)-Enabled Medical Devices. [(accessed on 21 October 2022)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/software-medical-device-samd/artific....
-
- Guermazi A., Tannoury C., Kompel A.J., Murakami A.M., Ducarouge A., Gillibert A., Li X., Tournier A., Lahoud Y., Jarraya M., et al. Improving Radiographic Fracture Recognition Performance and Efficiency Using Artificial Intelligence. Radiology. 2021;302:627–636. doi: 10.1148/radiol.210937. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duron L., Ducarouge A., Gillibert A., Laine J., Allouche C., Cherel N., Zhang Z., Nitche N., Lacave E., Pourchot A., et al. Assessment of an AI Aid in Detection of Adult Appendicular Skeletal Fractures by Emergency Physicians and Radiologists: A Multicenter Cross-sectional Diagnostic Study. Radiology. 2021;300:120–129. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021203886. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

