Enhanced Room-Temperature Thermoelectric Performance of 2D-SnSe Alloys via Electric-Current-Assisted Sintering
- PMID: 36676246
- PMCID: PMC9865124
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16020509
Enhanced Room-Temperature Thermoelectric Performance of 2D-SnSe Alloys via Electric-Current-Assisted Sintering
Abstract
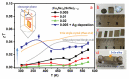
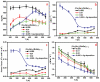
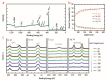
Single-crystalline tin-selenide (SnSe) has emerged as a high-performance and eco-friendly alternative to the lead-chalcogens often used in mid-temperature thermoelectric (TE) generators. At high temperature >800 K, the phase transition from Pnma to Cmcm causes a significant rise in the TE figure-of-merit (zT) curve. Conversely, the SnSe TE requires a booster at low temperatures, which allows broader applicability from a device perspective. Herein, a synergy of Cu alloy and Ag-coating is realized through a sequential multi-step synthesis, designed to combine different metal deposition effects. Single-crystalline (Cu2Se)x(SnSe)1−x alloys grown by the Bridgman method were then coated with a thin Ag layer by radio frequency (RF) sputtering, and the interlayer epitaxial film was observed via electric-current assisted sintering (ECAS). Consequently, the thin Ag-coating improves the electrical conductivity (σ) and reduces the thermal conductivity (κ) for (Cu2Se)0.005(SnSe)0.995+Ag alloy, increasing the zT curve at close to room temperature (373 K). The incorporation of multistep addition by ECAS enables tuning of the overall solubility of the alloy, which opens a new avenue to optimize TE performance in anisotropic 2D materials.
Keywords: 2D materials; SnSe single crystal; multistep deposition; radio frequency sputtering; thermoelectrics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thin Film Tin Selenide (SnSe) Thermoelectric Generators Exhibiting Ultralow Thermal Conductivity.Adv Mater. 2018 Aug;30(31):e1801357. doi: 10.1002/adma.201801357. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 29931697
-
Influence of Sputtering Power on the Properties of Magnetron Sputtered Tin Selenide Films.Materials (Basel). 2024 Jun 26;17(13):3132. doi: 10.3390/ma17133132. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998215 Free PMC article.
-
Full Thermoelectric Characterization of Stoichiometric Electrodeposited Thin Film Tin Selenide (SnSe).ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Jun 24;12(25):28232-28238. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c06026. Epub 2020 Jun 12. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32479049
-
High-Performance Thermoelectrics Based on Solution-Grown SnSe Nanostructures.ACS Nano. 2022 Jan 25;16(1):7-14. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c10584. Epub 2021 Dec 17. ACS Nano. 2022. PMID: 34919391 Review.
-
High-Performance Thermoelectric SnSe: Aqueous Synthesis, Innovations, and Challenges.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020 Feb 13;7(7):1902923. doi: 10.1002/advs.201902923. eCollection 2020 Apr. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020. PMID: 32274303 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seebeck T.J. Magnetische Polarisation der Metalle und Erze durch Temperatur-Differenz. Leopold Classic Library; South Yarra, Australia: 1822. pp. 265–373. Abhandlungen der Koniglichen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin. (In German)
-
- Li L., Han W., Pi L., Niu P., Han J., Wang C., Su B., Li H., Xiong J., Bando Y., et al. Emerging in-plane anisotropic two-dimensional materials. InfoMat. 2019;1:54–73. doi: 10.1002/inf2.12005. - DOI
-
- Mori H., Usui H., Ochi M., Kuroki K. Temperature-and doping-dependent roles of valleys in the thermoelectric performance of SnSe: A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B. 2017;96:085113. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.96.085113. - DOI
-
- Hou S., Li Z., Xue Y., Ning X., Wang J., Wang S. Surprisingly high in-plane thermoelectric performance in a-axisoriented epitaxial SnSe thin films. Mater. Today Phys. 2021;18:100399. doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2021.100399. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

