Isolation of Carboxylic Acids and NaOH from Kraft Black Liquor with a Membrane-Based Process Sequence
- PMID: 36676899
- PMCID: PMC9863791
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes13010092
Isolation of Carboxylic Acids and NaOH from Kraft Black Liquor with a Membrane-Based Process Sequence
Abstract
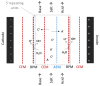
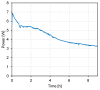
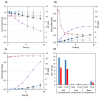
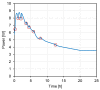
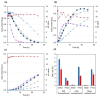
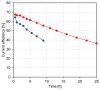
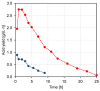
In kraft pulping, large quantities of biomass degradation products dissolved in the black liquor are incinerated for power generation and chemical recovery. The black liquor is, however, a promising feedstock for carboxylic acids and lignin. Efficient fractionation of black liquor can be used to isolate these compounds and recycle the pulping chemicals. The present work discusses the fractionation of industrial black liquor by a sequence of nanofiltration and bipolar membrane electrodialysis units. Nanofiltration led to retention of the majority of lignin in the retentate and to a significant concentration increase in low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids, such as formic, acetic, glycolic and lactic acids, in the permeate. Subsequent treatment with bipolar membrane electrodialysis showed the potential for simultaneous recovery of acids in the acid compartment and the pulping chemical NaOH in the base compartment. The residual lignin was completely retained by the used membranes. Diffusion of acids to the base compartment and the low current density, however, limited the yield of acids and the current efficiency. In experiments with a black liquor model solution under optimized conditions, NaOH and acid recoveries of 68-72% were achieved.
Keywords: biorefinery; bipolar membrane electrodialysis; black liquor; carboxylic acids; lignin; nanofiltration.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrochemical acidification of Kraft black liquor by electrodialysis with bipolar membrane: Ion exchange membrane fouling identification and mechanisms.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Feb 15;488:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.10.015. Epub 2016 Oct 11. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 27821338
-
Low-Molecular-Weight Lignin Recovery with Nanofiltration in the Kraft Pulping Process.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Mar 9;12(3):310. doi: 10.3390/membranes12030310. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35323785 Free PMC article.
-
Green chemicals from pulp production black liquor by partial wet oxidation.Waste Manag Res. 2015 Nov;33(11):1015-21. doi: 10.1177/0734242X15602807. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Waste Manag Res. 2015. PMID: 26377325
-
Recent developments in the application of kraft pulping alkaline chemicals for lignocellulosic pretreatment: Potential beneficiation of green liquor dregs waste.Bioresour Technol. 2020 Jun;306:123225. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123225. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Bioresour Technol. 2020. PMID: 32241680 Review.
-
Microbial valorization of kraft black liquor for production of platform chemicals, biofuels, and value-added products: A critical review.J Environ Manage. 2024 Aug;366:121631. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121631. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Environ Manage. 2024. PMID: 38986370 Review.
Cited by
-
Medicago Sativa Stems-A Multi-Output Integrated Biorefinery Approach.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 19;17(12):1709. doi: 10.3390/polym17121709. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40574236 Free PMC article.
-
Lignin Recovery from Black Liquor Using Integrated UF/NF Processes and Economic Analysis.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Feb 16;13(2):237. doi: 10.3390/membranes13020237. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36837740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Heiningen A. Converting a kraft pulp mill into an interated forest biorefinery. Pulp Pap. Can. 2006;6:141–146.
-
- Kumar H. Novel Concepts on the Recovery of By-Products from Alkaline Pulping. University of Jyväskylä; Jyväskylä, Finland: 2016. Research Report No. 198.
-
- Alén R. 40 Years Recovery Boiler Co-Operation in Finland. Suomen Soodakattilayhdistys Finnish Recovery Boiler Committee; Porvoo, Finland: 2004. Combustion Behaviour of Black Liquors from Different Delignification Conditions; pp. 31–42.
-
- Sixta H., Potthast A., Krotschek A. Chemical Pulping Processes. In: Sixta H., editor. Handbook of Pulp. Volume 1. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim, Germany: 2006. pp. 109–475. - DOI
-
- Bajpai P. Pulping Fundamentals. In: Bajpai P., editor. Biermann’s Handbook of Pulp and Paper Vol. 1 Raw Material and Pulp Making. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. pp. 295–351. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

