Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Circadian Clock Disruption, and Metabolic Consequences
- PMID: 36676985
- PMCID: PMC9863434
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo13010060
Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Circadian Clock Disruption, and Metabolic Consequences
Abstract
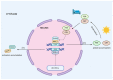
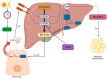
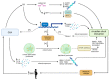
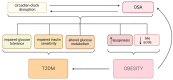
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a chronic disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of apnea and hypopnea during sleep. It is associated with various cardiovascular and metabolic complications, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. Many pathways can be responsible for T2DM development in OSA patients, e.g., those related to HIF-1 and SIRT1 expression. Moreover, epigenetic mechanisms, such as miRNA181a or miRNA199, are postulated to play a pivotal role in this link. It has been proven that OSA increases the occurrence of circadian clock disruption, which is also a risk factor for metabolic disease development. Circadian clock disruption impairs the metabolism of glucose, lipids, and the secretion of bile acids. Therefore, OSA-induced circadian clock disruption may be a potential, complex, underlying pathway involved in developing and exacerbating metabolic diseases among OSA patients. The current paper summarizes the available information pertaining to the relationship between OSA and circadian clock disruption in the context of potential mechanisms leading to metabolic disorders.
Keywords: OSA; circadian disruption; diabetes mellitus; metabolic complications; microRNA; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

