Lipidomic Predictors of Coronary No-Reflow
- PMID: 36677004
- PMCID: PMC9861202
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo13010079
Lipidomic Predictors of Coronary No-Reflow
Abstract
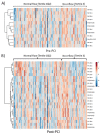
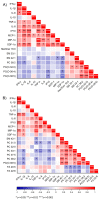
The ‘no-reflow’ phenomenon (NRP) after primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a serious complication among acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients. Herein, a comprehensive lipidomics approach was used to quantify over 300 distinct molecular species in circulating plasma from 126 patients with STEMI before and after primary PCI. Our analysis showed that three lipid classes: phosphatidylcholine (PC), alkylphosphatidylcholine (PC(O)), and sphingomyelin (SM), were significantly elevated (p < 0.05) in no-reflow patients before primary PCI. The levels of individual fatty acids and total fatty acid levels were significantly lower (p < 0.05) in no-reflow subjects after PCI. The grouping of patients based on ECG ST-segment resolution (STR) also demonstrated the same trend, confirming the possible role of these differential lipids in the setting of no-reflow. Sphingomyelin species, SM 41:1 and SM 41:2, was invariably positively correlated with corrected TIMI frame count (CTFC) at pre-PCI and post-PCI. The plasma levels of SM 42:1 exhibited an inverse association (p < 0.05) consistently with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) at pre-PCI and post-PCI. In conclusion, we identified plasma lipid profiles that distinguish individuals at risk of no-reflow and provided novel insights into how dyslipidemia may contribute to NRP after primary PCI.
Keywords: ether-lipids; lipidomics; no-reflow; sphingomyelin.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict relevant to the contents of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Elbendary M.A.W., Saleh M.A., Sabet S.S., Bastawy I. Correlation between endothelial dysfunction and occurrence of no-reflow in patients undergoing post-thrombolysis early invasive percutaneous intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Egypt Heart J. 2022;74:70. doi: 10.1186/s43044-022-00309-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Savic L., Mrdovic I., Asanin M., Stankovic S., Lasica R., Krljanac G., Rajic D., Simic D. The Impact of Kidney Function on the Slow-Flow/No-Reflow Phenomenon in Patients Treated with Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Registry Analysis. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2022;2022:5815274. doi: 10.1155/2022/5815274. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

