Influence of Polyvinylpyrrolidone on Thermoelectric Properties of Melt-Mixed Polymer/Carbon Nanotube Composites
- PMID: 36677242
- PMCID: PMC9863564
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14010181
Influence of Polyvinylpyrrolidone on Thermoelectric Properties of Melt-Mixed Polymer/Carbon Nanotube Composites
Abstract
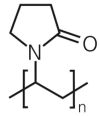
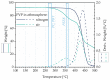
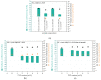
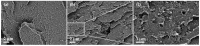
For thermoelectric applications, both p- and n-type semi-conductive materials are combined. In melt-mixed composites based on thermoplastic polymers and carbon nanotubes, usually the p-type with a positive Seebeck coefficient (S) is present. One way to produce composites with a negative Seebeck coefficient is to add further additives. In the present study, for the first time, the combination of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in melt-mixed composites is investigated. Polycarbonate (PC), poly(butylene terephthalate) (PBT), and poly(ether ether ketone) (PEEK) filled with SWCNTs and PVP were melt-mixed in small scales and thermoelectric properties of compression moulded plates were studied. It could be shown that a switch in the S-value from positive to negative values was only possible for PC composites. The addition of 5 wt% PVP shifted the S-value from 37.8 µV/K to -31.5 µV/K (2 wt% SWCNT). For PBT as a matrix, a decrease in the Seebeck coefficient from 59.4 µV/K to 8.0 µV/K (8 wt% PVP, 2 wt% SWCNT) could be found. In PEEK-based composites, the S-value increased slightly with the PVP content from 48.0 µV/K up to 54.3 µV/K (3 wt% PVP, 1 wt% SWCNT). In addition, the long-term stability of the composites was studied. Unfortunately, the achieved properties were not stable over a storage time of 6 or 18 months. Thus, in summary, PVP is not suitable for producing long-term stable, melt-mixed n-type SWCNT composites.
Keywords: electron doping; nanotubes; polymer composites; thermoelectric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

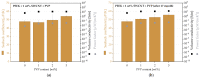

References
-
- Rowe D.M. CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 1995.
-
- Goldsmid H.J. Introduction to Thermoelectricity. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2010. - DOI
-
- Nolas G.S., Sharp J., Goldsmid H. Thermoelectrics. Basic Principles and New Materials Developments. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2001.
-
- Luo J., Krause B., Pötschke P. Melt-mixed thermoplastic composites containing carbon nanotubes for thermoelectric applications. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2016;3:1107–1116. doi: 10.3934/matersci.2016.3.1107. - DOI
-
- Luo J., Cerretti G., Krause B., Zhang L., Otto T., Jenschke W., Ullrich M., Tremel W., Voit B., Pötschke P. Polypropylene-based melt mixed composites with singlewalled carbon nanotubes for thermoelectric applications: Switching from p-type to n-type by the addition of polyethylene glycol. Polymer. 2017;108:513–520. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2016.12.019. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

