microRNAs: Critical Players during Helminth Infections
- PMID: 36677353
- PMCID: PMC9861972
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11010061
microRNAs: Critical Players during Helminth Infections
Abstract
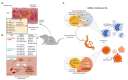
microRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally through their interaction with the 3' untranslated regions (3' UTR) of target mRNAs, affecting their stability and/or translation. Therefore, miRNAs regulate biological processes such as signal transduction, cell death, autophagy, metabolism, development, cellular proliferation, and differentiation. Dysregulated expression of microRNAs is associated with infectious diseases, where miRNAs modulate important aspects of the parasite-host interaction. Helminths are parasitic worms that cause various neglected tropical diseases affecting millions worldwide. These parasites have sophisticated mechanisms that give them a surprising immunomodulatory capacity favoring parasite persistence and establishment of infection. In this review, we analyze miRNAs in infections caused by helminths, emphasizing their role in immune regulation and its implication in diagnosis, prognosis, and the development of therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Brugia; Fasciola; Schistosoma; immunomodulation; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Vidal-Anzardo M., Yagui Moscoso M., Beltrán Fabian M., Vidal-Anzardo M., Yagui Moscoso M., Beltrán Fabian M. Parasitosis Intestinal: Helmintos. Prevalencia y Análisis de La Tendencia de Los Años 2010 a 2017 En El Perú. An. De La Fac. De Med. 2020;81:26–32. doi: 10.15381/anales.v81i1.17784. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

