Viral and Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Israel
- PMID: 36677458
- PMCID: PMC9864990
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11010166
Viral and Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Israel
Abstract
Background: previous worldwide reports indicated a substantial short-term reduction in various respiratory infections during the early phase of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
Aims: exploring the long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on respiratory pathogens.
Methods: retrospective analysis of bacterial and viral positivity rate in respiratory samples, between 1 January 2017-30 June 2022 in a tertiary hospital in Jerusalem, Israel.
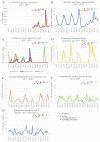
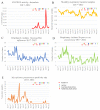
Results: A decline in overall respiratory tests and positivity rate was observed in the first months of the pandemic. Respiratory isolations of Hemophilus influenza and Streptococcus pneumoniae were insignificantly affected and returned to their monthly average by November 2020, despite a parallel surge in COVID-19 activity, while Mycoplasma pneumoniae was almost eliminated from the respiratory pathogens scene. Each viral pathogen acted differently, with adenovirus affected only for few months. Human-metapneumovirus and respiratory-syncytial-virus had reduced activity for approximately a year, and influenza A virus resurged in November 2021 with the elimination of Influenza-B.
Conclusions: After an immediate decline in non-SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections, each pathogen has a different pattern during a 2-year follow-up. These patterns might be influenced by intrinsic factors of each pathogen and different risk reduction behaviors of the population. Since some of these measures will remain in the following years, we cannot predict the timing of return to pre-COVID-19 normalcy.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; bacterial; respiratory pathogens; viral.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ghebreyesus D.T.A. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. 2020. [(accessed on 25 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera....
-
- Oster Y., Michael-Gayego A., Rivkin M., Levinson L., Wolf D.G., Nir-Paz R. Decreased prevalence rate of respiratory pathogens in hospitalized patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: Possible role for public health containment measures? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020;27:811–812. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.12.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuitunen I., Artama M., Makela L., Backman K., Heiskanen-Kosma T., Renko M. Effect of Social Distancing Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Incidence of Viral Respiratory Tract Infections in Children in Finland During Early 2020. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020;39:e423–e427. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002845. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angoulvant F., Ouldali N., Yang D.D., Filser M., Gajdos V., Rybak A., Guedj R., Soussan-Banini V., Basmaci R., Lefevre-Utile A., et al. Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: Impact Caused by School Closure and National Lockdown on Pediatric Visits and Admissions for Viral and Nonviral Infections—A Time Series Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021;72:319–322. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa710. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friedrich F., Ongaratto R., Scotta M.C., Veras T.N., Stein R.T., Lumertz M.S., Jones M.H., Comaru T., Pinto L.A. Early Impact of Social Distancing in Response to Coronavirus Disease 2019 on Hospitalizations for Acute Bronchiolitis in Infants in Brazil. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021;72:2071–2075. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1458. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

