Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Studies of Naphthoquinone Sulfonamides and Sulfonate Ester Derivatives as P2X7 Inhibitors
- PMID: 36677652
- PMCID: PMC9866630
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28020590
Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Studies of Naphthoquinone Sulfonamides and Sulfonate Ester Derivatives as P2X7 Inhibitors
Abstract
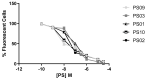
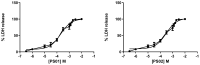
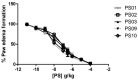
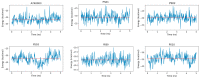
ATP acts in the extracellular environment as an important signal, activating a family of receptors called purinergic receptors. In recent years, interest in the potential therapeutics of purinergic components, including agonists and antagonists of receptors, has increased. Currently, many observations have indicated that ATP acts as an important mediator of inflammatory responses and, when found in high concentrations in the extracellular space, is related to the activation of the P2X7 purinergic receptor. In this sense, the search for new inhibitors for this receptor has attracted a great deal of attention in recent years. Sulfonamide derivatives have been reported to be potent inhibitors of P2X receptors. In this study, ten naphthoquinone sulfonamide derivatives and five naphthoquinone sulfonate ester derivatives were tested for their inhibitory activity on the P2X7 receptor expressed in peritoneal macrophages. Some compounds showed promising results, displaying IC50 values lower than that of A740003. Molecular docking and dynamic studies also indicated that the active compounds bind to an allosteric site on P2X7R. The binding free energy indicates that sulfonamides have an affinity for the P2X7 receptor similar to A740003. Therefore, the compounds studied herein present potential P2X7R inhibition.
Keywords: ATP; biomass; heterocycles; inflammation; naphthoquinones; sulfonamides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Burnstock G., Williams M. P2 purinergic receptors: Modulation of cell function and therapeutic potential. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000;295:862–869. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 316568/2021-0/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- Financial Code 001/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- E-26/203.246/2017/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- E-26/211.025/2019/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- E-26/200.982/2021/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

