Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Modern Industry
- PMID: 36677717
- PMCID: PMC9865684
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28020661
Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Modern Industry
Abstract
Nanotechnology, contrary to its name, has massively revolutionized industries around the world. This paper predominantly deals with data regarding the applications of nanotechnology in the modernization of several industries. A comprehensive research strategy is adopted to incorporate the latest data driven from major science platforms. Resultantly, a broad-spectrum overview is presented which comprises the diverse applications of nanotechnology in modern industries. This study reveals that nanotechnology is not limited to research labs or small-scale manufacturing units of nanomedicine, but instead has taken a major share in different industries. Companies around the world are now trying to make their innovations more efficient in terms of structuring, working, and designing outlook and productivity by taking advantage of nanotechnology. From small-scale manufacturing and processing units such as those in agriculture, food, and medicine industries to larger-scale production units such as those operating in industries of automobiles, civil engineering, and environmental management, nanotechnology has manifested the modernization of almost every industrial domain on a global scale. With pronounced cooperation among researchers, industrialists, scientists, technologists, environmentalists, and educationists, the more sustainable development of nano-based industries can be predicted in the future.
Keywords: agriculture; automobiles; biotechnology; construction; cosmetics industry; environment; foods; medicine; nanoindustries; nanotechnology; textile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
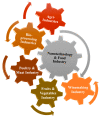

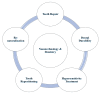
References
-
- Rickerby D., Morrison M. Nanotechnology and the environment: A European perspective. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2007;8:19. doi: 10.1016/j.stam.2006.10.002. - DOI
-
- Bhushan B. Handbook of Nanotechnology. Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2017. Introduction to nanotechnology; pp. 1–19.
-
- Kumar S. Nanotechnology in computers. Int. J. Inf. Comput. Technol. 2014;4:974–2239.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

