Sericultural By-Products: The Potential for Alternative Therapy in Cancer Drug Design
- PMID: 36677907
- PMCID: PMC9861160
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28020850
Sericultural By-Products: The Potential for Alternative Therapy in Cancer Drug Design
Abstract
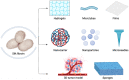
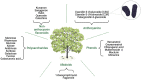
Major progress has been made in cancer research; however, cancer remains one of the most important health-related burdens. Sericulture importance is no longer limited to the textile industry, but its by-products, such as silk fibroin or mulberry, exhibit great impact in the cancer research area. Fibroin, the pivotal compound that is found in silk, owns superior biocompatibility and biodegradability, representing one of the most important biomaterials. Numerous studies have reported its successful use as a drug delivery system, and it is currently used to develop three-dimensional tumor models that lead to a better understanding of cancer biology and play a great role in the development of novel antitumoral strategies. Moreover, sericin's cytotoxic effect on various tumoral cell lines has been reported, but also, it has been used as a nanocarrier for target therapeutic agents. On the other hand, mulberry compounds include various bioactive elements that are well known for their antitumoral activities, such as polyphenols or anthocyanins. In this review, the latest progress of using sericultural by-products in cancer therapy is discussed by highlighting their notable impact in developing novel effective drug strategies.
Keywords: 3D models; biomaterials; cancer therapy; mulberry; silk fibroin; silkworms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

