Role of Vitamin D Deficiency in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases
- PMID: 36678205
- PMCID: PMC9864832
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15020334
Role of Vitamin D Deficiency in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases
Abstract
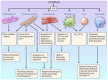
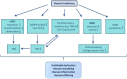
Deficiency in vitamin D (VitD), a lipid-soluble vitamin and steroid hormone, affects approximately 24% to 40% of the population of the Western world. In addition to its well-documented effects on the musculoskeletal system, VitD also contributes importantly to the promotion and preservation of cardiovascular health via modulating the immune and inflammatory functions and regulating cell proliferation and migration, endothelial function, renin expression, and extracellular matrix homeostasis. This brief overview focuses on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects of VitD and the cellular, molecular, and functional changes that occur in the circulatory system in VitD deficiency (VDD). It explores the links among VDD and adverse vascular remodeling, endothelial dysfunction, vascular inflammation, and increased risk for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Improved understanding of the complex role of VDD in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, stroke, and vascular cognitive impairment is crucial for all cardiologists, dietitians, and geriatricians, as VDD presents an easy target for intervention.
Keywords: VCI; aging; cerebral circulation; cerebrovascular disease; cholecalciferol; ergocalciferol; hypertension; stroke; vascular cognitive impairment; vitamin D; vitamin D2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- da Silveira E.A., Moura L., Castro M.C.R., Kac G., Hadler M., Noll P., Noll M., Rezende A.T.O., Delpino F.M., Oliveira C. Prevalence of Vitamin D and Calcium Deficiency and Insufficiency in Women of Childbearing Age and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2022;14:4351. doi: 10.3390/nu14204351. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K-125174/Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office
- K-139230/Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office
- PD-143327/Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office
- ÚNKP-22-4-II-SE-17/Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the NRDI Fund
- 2020-1.1.6-JÖVŐ-2021-00010/Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the NRDI Fund
- 2020-1.1.6-JÖVŐ-2021-00013/Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the NRDI Fund
- TKP2021-NKTA-47/Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the NRDI Fund
- RRF-2.3.1-21-2022-00003/Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the NRDI Fund
- TKP2021-EGA-25/Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the NRDI Fund
- STIA-KFI-2021/Semmelweis Science and Innovation Fund
- STIA-OTKA-2021/Semmelweis Science and Innovation Fund
- 101004093/ EUniWell/EAC-A02-2019 / EAC-A02-2019-1/European University for Well-Being (EUniWell) program
- R01AG055395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG068295/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG070915/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS100782/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA255840/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

