Consumption of Eggs Alone or Enriched with Annatto (Bixa orellana L.) Does Not Increase Cardiovascular Risk in Healthy Adults-A Randomized Clinical Trial, the Eggant Study
- PMID: 36678239
- PMCID: PMC9865189
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15020369
Consumption of Eggs Alone or Enriched with Annatto (Bixa orellana L.) Does Not Increase Cardiovascular Risk in Healthy Adults-A Randomized Clinical Trial, the Eggant Study
Abstract
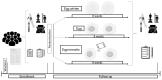
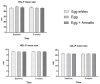
Most atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases can be prevented by modifying lifestyles, including unhealthy diets. Eggs contain important carotenoids that may impact cardiovascular risk. The lipid nature of eggs can improve the bioavailability of other carotenoids, such as Annatto (Bixa orellana L.), with reported antioxidant properties. Although numerous studies have shown that there is no association between egg consumption and cardiovascular risk, there is still controversy. In addition, there is limited information about Annatto's effects on human health. This study evaluated the association between egg consumption and its enrichment with Annatto in lipid biomarkers of cardiovascular disease. In a parallel clinical trial, one hundred and five (n = 105) men and women were randomized by age, sex, and body mass index (BMI), and distributed into three groups. Subjects consumed daily, for 8 weeks, either two eggs, two eggs with Annatto, or two egg whites. Plasma lipids were measured by enzymatic colorimetric methods, plasma apolipoproteins and lipoprotein subfractions and size by nuclear magnetic resonance. There were no differences between groups in age, sex, and BMI. No significant changes were found over time or between groups in plasma triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein (apo) A1, apo B, or lipoprotein subfraction concentrations. In healthy adults, the intake of two eggs a day, or two eggs with Annatto for eight weeks, did not generate adverse changes in cardiovascular risk markers.
Keywords: Bixa orellana; annatto; apolipoproteins; blood lipids; cardiovascular risk; carotenoids; eggs; lipid biomarkers; lipoproteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Avinal had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Annatto-Enriched Egg Improves the Perception of Satiety in Healthy Adults-Randomized Clinical Trial: EGGANT Study.Foods. 2024 Feb 28;13(5):731. doi: 10.3390/foods13050731. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472844 Free PMC article.
-
Compared to an Oatmeal Breakfast, Two Eggs/Day Increased Plasma Carotenoids and Choline without Increasing Trimethyl Amine N-Oxide Concentrations.J Am Coll Nutr. 2018 Feb;37(2):140-148. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2017.1365026. Epub 2018 Jan 9. J Am Coll Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29313753 Clinical Trial.
-
A two-year clinical study of the effects of two triphasic oral contraceptives on plasma lipids.Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud. 1994 Sep-Oct;39(5):283-91. Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud. 1994. PMID: 7820162 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of whole egg intake on blood pressure, lipids and lipoproteins in middle-aged and older population: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2019 Jul;29(7):653-664. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2019.04.004. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 31076323
-
The responses of different dosages of egg consumption on blood lipid profile: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.J Food Biochem. 2020 Aug;44(8):e13263. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13263. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Food Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32524644
Cited by
-
Annatto-Enriched Egg Improves the Perception of Satiety in Healthy Adults-Randomized Clinical Trial: EGGANT Study.Foods. 2024 Feb 28;13(5):731. doi: 10.3390/foods13050731. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472844 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of dietary interventions on cardiometabolic health.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 May 31;24(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02766-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40450314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Dietary Folic Acid Supplementation Reduced the Composition of Fatty Acids and Amino Acids in Fortified Eggs.Foods. 2024 Mar 29;13(7):1048. doi: 10.3390/foods13071048. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38611353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powell-Wiley T.M., Poirier P., Burke L.E., Després J.-P., Gordon-Larsen P., Lavie C.J., Lear S.A., Ndumele C.E., Neeland I.J., Sanders P., et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:E984–E1010. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000973. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social. Instituto Colombiano de Bienestar Familiar (ICBF) Instituto Nacional de Salud . Encuesta Nacional de la Situación Nutricional en Colombia-ENSIN 2010. Da Vinci Editores & CÍA S N C; Bogotá, Colombia: 2011. p. 365.
-
- Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social. Instituto Nacional de Salud. Instituto Colombiano de Bienestar Familiar (ICBF) Universidad Nacional de Colombia . Encuesta Nacional de la Situación Nutricional—ENSIN 2015. Editores & CÍA S N C; Bogotá, Colombia: 2020. p. 683.
-
- Chacón C., Ramírez M. Poverty in Colombia, in times of COVID-19. Munich Pers RePEc Arch. 2020;11:1–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

