Identification of YABBY Transcription Factors and Their Function in ABA and Salinity Response in Nelumbo nucifera
- PMID: 36679092
- PMCID: PMC9866709
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12020380
Identification of YABBY Transcription Factors and Their Function in ABA and Salinity Response in Nelumbo nucifera
Abstract
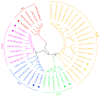
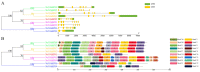
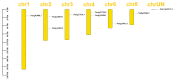
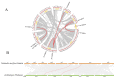
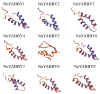
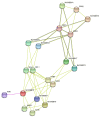
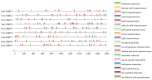
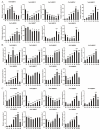
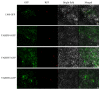
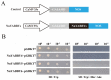
The plant-specific transcription factor family YABBY plays important roles in plant responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Although the function of YABBY has been identified in many species, systematic analysis in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) is still relatively lacking. The present study aimed to characterize all of the YABBY genes in lotus and obtain better insights into NnYABBYs in response to salt stress by depending on ABA signaling. Here, we identified nine YABBY genes by searching the whole lotus genome based on the conserved YABBY domain. Further analysis showed that these members were distributed on six different chromosomes and named from YABBY1 to YABBY9, which were divided into five subgroups, including YAB1, YAB2, YAB5, INO, and CRC. The analysis of cis-elements in promotors revealed that NnYABBYs could be involved in plant hormone signaling and plant responses to abiotic stresses. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) showed that NnYABBYs could be up-regulated or down-regulated by ABA, fluridone, and salt treatment. Subcellular localization indicated that NnYABBY4, NnYABBY5, and NnYABBY6 were mainly localized in the cell membrane and cytoplasm. In addition, the intrinsic trans-activity of NnYABBY was tested by a Y2H assay, which revealed that NnYABBY4, NnYABBY5, and NnYABBY6 are deprived of such a property. This study provided a theoretical basis and reference for the functional research of YABBY for the molecular breeding of lotus.
Keywords: ABA; Nelumbo nucifera; YABBY; salt stress; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shukla S., Park J., Park J.H., Lee J.S., Kim M. Development of lotus root fermented sugar syrup as a functional food supplement/condiment and evaluation of its physicochemical, nutritional and microbiological properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018;55:619–629. doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2971-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

