Population-Based Analysis of the Immunoglobulin G Response to Different COVID-19 Vaccines in Brazil
- PMID: 36679871
- PMCID: PMC9862407
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11010021
Population-Based Analysis of the Immunoglobulin G Response to Different COVID-19 Vaccines in Brazil
Abstract
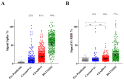
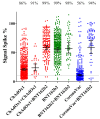
(1) Background: COVID-19 vaccination in Brazil has been performed mostly with CoronaVac (Sinovac), ChAdOx1-S (AstraZeneca-University of Oxford) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccines. The titers of IgG antibodies reactive to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein correlate with vaccine efficacy. Studies comparing vaccine immunogenicity in a real-world scenario are lacking. (2) Methods: We performed a population-based study to analyze the immunoglobulin G response to different COVID-19 vaccines. Citizens older than 18 years (n = 2376) provided personal data, a self-declaration of any previous COVID-19 positive tests and information regarding COVID-19 vaccination: the vaccine popular name and the date of each dose. Blood samples were collected and the levels of IgG reactive to SARS-CoV-2 antigens were determined and compared between different vaccine groups. (3) Results: The seroconversion for anti-spike IgG achieved > 95% by February 2022 and maintained stable until June 2022. Higher anti-spike IgG titers were detected in individuals vaccinated with BNT162b2, followed by ChAdOx1-S and CoronaVac. The anti-spike IgG response was negatively correlated with age and interval after the second dose for the BNT162b2 vaccine. Natural infections boosted anti-spike IgG in those individuals who completed primary vaccination with ChAdOx1-S and CoronaVac, but not with BNT162b2. The levels of anti-spike IgG increased with the number of vaccine doses administered. The application of BNT162b2 as a 3rd booster dose resulted in high anti-spike IgG antibody titers, despite the type of vaccine used during primary vaccination. (4) Conclusions: Our data confirmed the effectiveness of the Brazilian vaccination program. Of the vaccines used in Brazil, BNT162b2 performed better to elicit anti-spike protein IgG after primary vaccination and as a booster dose and thus should be recommended as a booster whenever available. A continuous COVID-19 vaccination program will be required to sustain anti-spike IgG antibodies in the population.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; humoral response; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
COVID-19 lateral flow IgG seropositivity and serum neutralising antibody responses after primary and booster vaccinations in Chile: a cross-sectional study.Lancet Microbe. 2023 Mar;4(3):e149-e158. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(22)00290-7. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Lancet Microbe. 2023. PMID: 36716754 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike receptor binding domain IgG antibody responses after CoronaVac, BNT162b2, ChAdOx1 COVID-19 vaccines, and a single booster dose: a prospective, longitudinal population-based study.Lancet Microbe. 2022 Apr;3(4):e274-e283. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00305-0. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Lancet Microbe. 2022. PMID: 35165669 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world serological responses to extended-interval and heterologous COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in frail, older people (UNCoVER): an interim report from a prospective observational cohort study.Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022 Mar;3(3):e166-e175. doi: 10.1016/S2666-7568(22)00012-5. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022. PMID: 35224524 Free PMC article.
-
MOG encephalomyelitis after vaccination against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2): case report and comprehensive review of the literature.J Neurol. 2022 Oct;269(10):5198-5212. doi: 10.1007/s00415-022-11194-9. Epub 2022 Jun 23. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35737110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Overweight/Obesity and the Safety and Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Review.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 May 17;11(5):996. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11050996. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37243100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A 20-month longitudinal study to evaluate humoral and cellular immunity after COVID-19 vaccines.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2025 Jul 18;120:e240193. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760240193. eCollection 2025. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2025. PMID: 40699035 Free PMC article.
-
Symptomatology and IgG Levels before and after SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Individuals.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Oct 8;12(10):1149. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12101149. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39460316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Voysey M., Clemens S.A.C., Madhi S.A., Weckx L.Y., Folegatti P.M., Aley P.K., Angus B., Baillie V.L., Barnabas S.L., Bhorat Q.E., et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet. 2021;397:99–111. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

