Impact of Improper Storage of ChAdOx1-S (AstraZeneca) Vaccine on Its Efficacy and Safety
- PMID: 36679938
- PMCID: PMC9865338
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11010093
Impact of Improper Storage of ChAdOx1-S (AstraZeneca) Vaccine on Its Efficacy and Safety
Abstract
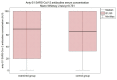
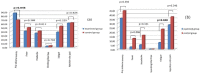
Background: In May 2021, there was an incident regarding giving patients AstraZeneca vaccines stored improperly. They were stored at room temperature (21 degrees centigrade) for 18 h, 12 h longer than the producer recommends. Aim of the study: The paper aims to contribute to the body of knowledge concerning the efficacy and safety of the ChAdOx1-S (AstraZeneca) vaccine concerning the requirements for cold supply chain specification. Patients and methods: Improperly stored vaccines were given to 44 patients, and 39 of them decided to take part in the study. The Control group consisted of 56 people vaccinated on the same days by the same medical teams, using properly stored medicines. Results: The concentration of anti-S1 SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein IgG antibodies did not differ significantly between the groups. Examined group median 70 kU/L (20;100). Control group median 66 kU/L (32.75;100), p = 0.751. We did not observe any COVID-19 infections in either the control or examined group for half a year after the incident. People from each group reported that local and systemic adverse events occurred directly after the first and second doses. In the control group, one case of spontaneously subsiding face edema and joint pain was observed. There were no severe or fatal adverse events. There were no significant differences between the groups, besides the fatigue, after the second dose. Conclusion: AstraZeneca vaccine ChAdOx1-S stored at 21 degrees centigrade for 18 h before vaccination has the same safety profile (p < 0.05) and the same efficacy (p < 0.05) as the vaccines stored in conditions recommended by the producer.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccination; ChAdOx1-S (AstraZeneca) vaccine; cold supply chain; vaccine efficacy; vaccine safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Wang X. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 MRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:1577–1578. - PubMed
-
- Meo S.A., Bukhari I.A., Akram J., Meo A.S., Klonoff D.C. COVID-19 Vaccines: Comparison of Biological, Pharmacological Characteristics and Adverse Effects of Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021;25:1663–1669. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous