Amphotericin B Nano-Assemblies Circumvent Intrinsic Toxicity and Ensure Superior Protection in Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis with Feeble Toxic Manifestation
- PMID: 36679946
- PMCID: PMC9866558
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11010100
Amphotericin B Nano-Assemblies Circumvent Intrinsic Toxicity and Ensure Superior Protection in Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis with Feeble Toxic Manifestation
Abstract
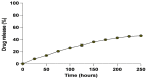
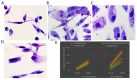
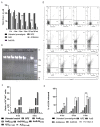
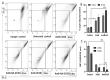
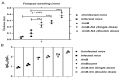
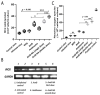
In spite of its high effectiveness in the treatment of both leishmaniasis as well as a range of fungal infections, the free form of the polyene antibiotic amphotericin B (AmB) does not entertain the status of the most preferred drug of choice in clinical settings. The high intrinsic toxicity of the principal drug could be considered the main impedance in the frequent medicinal use of this otherwise very effective antimicrobial agent. Taking into consideration this fact, the pharma industry has introduced many novel dosage forms of AmB to alleviate its toxicity issues. However, the limited production, high cost, requirement for a strict cold chain, and need for parenteral administration are some of the limitations that explicitly compel professionals to look for the development of an alternate dosage form of this important drug. Considering the fact that the nano-size dimensions of drug formulation play an important role in increasing the efficacy of the core drug, we employed a green method for the development of nano-assemblies of AmB (AmB-NA). The as-synthesized AmB-NA manifests desirable pharmacokinetics in the treated animals. The possible mechanistic insight suggested that as-synthesized AmB-NA induces necrosis-mediated cell death and severe mitochondrial dysfunction in L. donovani promastigotes by triggering depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential. In vivo studies demonstrate a noticeable decline in parasite burden in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow of the experimental BALB/c mice host. In addition to successfully suppressing the Leishmania donovani, the as-formed AmB-NA formulation also modulates the host immune system with predominant Th1 polarization, a key immune defender that facilitates the killing of the intracellular parasite.
Keywords: Th1 polarization; drug delivery; green synthesis; nano assembly; nano-assembled anti-leishmanial drug; nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Complete cure of experimental visceral leishmaniasis with amphotericin B in stearylamine-bearing cationic liposomes involves down-regulation of IL-10 and favorable T cell responses.J Immunol. 2008 Jul 15;181(2):1386-98. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.2.1386. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18606693
-
Amphotericin B-gum arabic conjugates: synthesis, toxicity, bioavailability, and activities against Leishmania and fungi.Pharm Res. 2007 May;24(5):971-80. doi: 10.1007/s11095-006-9222-z. Epub 2007 Mar 20. Pharm Res. 2007. PMID: 17372682
-
Amphotericin B: A drug of choice for Visceral Leishmaniasis.Acta Trop. 2022 Nov;235:106661. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2022.106661. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Acta Trop. 2022. PMID: 35998680 Review.
-
Leishmanicidal activity of amphotericin B encapsulated in PLGA-DMSA nanoparticles to treat cutaneous leishmaniasis in C57BL/6 mice.Exp Parasitol. 2013 Oct;135(2):217-22. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Exp Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23891944
-
Limitations of current chemotherapy and future of nanoformulation-based AmB delivery for visceral leishmaniasis-An updated review.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 14;10:1016925. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1016925. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36588956 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Diterpene Polyalthic Acid Combined with Amphotericin B against Leishmania amazonensis In Vitro.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;17(9):1243. doi: 10.3390/ph17091243. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338405 Free PMC article.
-
Disclosing the Antifungal Mechanisms of the Cyclam Salt H4[H2(4-CF3PhCH2)2Cyclam]Cl4 against Candida albicans and Candida krusei.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 10;25(10):5209. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105209. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791254 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Robust Systems for Lupeol Delivery in the Treatment of Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;16(12):1646. doi: 10.3390/ph16121646. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leishmaniasis, WHO 2021. [(accessed on 19 October 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

