Epizootic Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype 8 in Tunisia, 2021
- PMID: 36680057
- PMCID: PMC9866946
- DOI: 10.3390/v15010016
Epizootic Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype 8 in Tunisia, 2021
Abstract
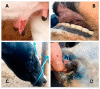
Epizootic haemorrhagic disease (EHD) is a Culicoides-borne viral disease caused by the epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV) associated with clinical manifestations in domestic and wild ruminants, primarily white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) and cattle (Bos taurus). In late September 2021, EHDV was reported in cattle farms in central/western Tunisia. It rapidly spread throughout the country with more than 200 confirmed outbreaks. We applied a combination of classical and molecular techniques to characterize the causative virus as a member of the serotype EHDV-8. This is the first evidence of EHDV- 8 circulation since 1982 when the prototype EHDV-8 strain was isolated in Australia. This work highlights the urgent need for vaccines for a range of EHDV serotypes.
Keywords: EHDV; EHDV serotype 8; Tunisia; circulation; virus characterization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply a recommendation or endorsement.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype 8 in Naturally Infected Barbary Deer (Cervus elaphus barbarus) and Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Tunisia.Viruses. 2023 Jul 18;15(7):1567. doi: 10.3390/v15071567. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37515253 Free PMC article.
-
The First 10 Years (2006-15) of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype 6 in the USA.J Wildl Dis. 2017 Oct;53(4):901-905. doi: 10.7589/2016-12-284. Epub 2017 Jun 28. J Wildl Dis. 2017. PMID: 28657859
-
Epidemiological Analyses of the First Incursion of the Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Serotype 8 in Tunisia, 2021-2022.Viruses. 2024 Feb 27;16(3):362. doi: 10.3390/v16030362. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543728 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on the Changing Landscape of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Control.Viruses. 2021 Nov 12;13(11):2268. doi: 10.3390/v13112268. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34835074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epizootic haemorrhagic disease.Rev Sci Tech. 2015 Aug;34(2):341-51. doi: 10.20506/rst.34.2.2361. Rev Sci Tech. 2015. PMID: 26601439 Review.
Cited by
-
Biting Midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) as Vectors of Viruses.Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 4;11(11):2706. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112706. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Risk of Windborne Dispersal of Culicoides Midges in Emerging Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Outbreaks in France.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2024 Jun 28;2024:5571195. doi: 10.1155/2024/5571195. eCollection 2024. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2024. PMID: 40303085 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogenous within-herd seroprevalence against epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus type 8 (EHDV-8) after massive virus circulation in cattle in France, 2023.Front Vet Sci. 2025 May 14;12:1562883. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1562883. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40438411 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance, Prevention, Evolution and Control of Emerging Viruses: A 2022 Editorial Update.Viruses. 2023 Oct 17;15(10):2098. doi: 10.3390/v15102098. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37896875 Free PMC article.
-
Description of the Clinical Findings Associated With the Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease in Cattle From Northwestern Spain During the Emergence.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025 May 24;2025:7808243. doi: 10.1155/tbed/7808243. eCollection 2025. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025. PMID: 40453457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacLachlan N.J. Bluetongue: Pathogenesis and duration of viraemia. Vet. Ital. 2004;40:462–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

