Genetic Characteristics of Measles Viruses Isolated in Taiwan between 2015 and 2020
- PMID: 36680251
- PMCID: PMC9863581
- DOI: 10.3390/v15010211
Genetic Characteristics of Measles Viruses Isolated in Taiwan between 2015 and 2020
Abstract
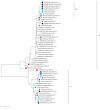
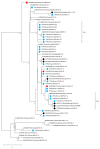
A genetic analysis of circulating measles virus (MeV) provides strong evidence of an interruption in endemic measles and supports the elimination status of this disease. This study investigated 219 MeVs isolated between 2015 and 2020. Based on the 450 nucleotide sequences of the nucleoprotein gene (N-450), three genotypes of the H1, D8 and B3 with 8, 18 and 6 different N-450 sequences, respectively, were identified. The H1 genotype virus has not circulated in Taiwan since 2017, and the D8 and B3 genotype MeVs became dominant between 2018 and 2019. Different D8 genotype variants were imported from neighboring countries, and the majority of MeV variants were detected only for a short period. However, MVs/Gir Somnath.IND/42.16[D8], a named strain designated by the World Health Organization (WHO), was detected over 2 years. To explore whether the endemic transmission of measles has been underestimated, another sequence window of the hypervariable, noncoding regions between the matrix (M) and fusion (F) genes (MF-NCR) was introduced to clarify the transmission chain. From the chronological sequence analysis of MeVs with N-450 and MF-NCR sequence windows, no endemic MeV variants lasted over 4 weeks, providing strong evidence to support the contention that Taiwan has reached the status for measles elimination.
Keywords: elimination; genotype; measles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Sequencing the Measles Virus Hemagglutinin Gene and Hypervariable Region in the Measles Outbreak Investigations in Sweden During 2013-2014.J Infect Dis. 2016 Feb 15;213(4):592-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv434. Epub 2015 Sep 7. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26347574
-
Measles outbreaks in 2017-2019 - molecular surveillance started in the Czech Republic.Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2022 Spring;71(1):40-47. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2022. PMID: 35477269 English.
-
Molecular epidemiology of measles virus in Taiwan in 2010-2011: the common genotype changed from H1 to D9 and the first appearance of D4.J Med Virol. 2013 Jun;85(6):1095-9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23563. J Med Virol. 2013. PMID: 23588738
-
Long-term transmission of measles virus in Central and continental Western Europe.Virus Genes. 2015 Feb;50(1):2-11. doi: 10.1007/s11262-015-1173-1. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Virus Genes. 2015. PMID: 25663095 Review.
-
Global genetic diversity of measles virus (Paramyxoviridae: Morbillivirus: Morbillivirus hominis): historical aspects and current state.Vopr Virusol. 2023 Nov 7;68(5):361-371. doi: 10.36233/0507-4088-187. Vopr Virusol. 2023. PMID: 38156571 Review.
Cited by
-
Measles Sequencing: Lessons Learned from a Large-Scale Outbreak.Viruses. 2025 Jun 27;17(7):913. doi: 10.3390/v17070913. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733531 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic tools for post-elimination measles molecular epidemiology using Canadian surveillance data from 2018-2020.Front Microbiol. 2024 Nov 19;15:1475144. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1475144. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39629208 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

