Expression of Long Non-Coding RNA H19 in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 36680478
- PMCID: PMC9868437
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2022.8315
Expression of Long Non-Coding RNA H19 in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
OObjective: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) H19 has essential roles in growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis of most cancers. H19 dysregulation is present in a large number of solid tumors and leukemia. However, the expression level of H19 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) has not been elucidated yet. The current study aimed to explore H19 expression in ALL patients and cell lines.
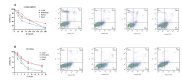
Materials and methods: This experimental study was conducted in bone marrow (BM) samples collected from 25 patients with newly diagnosed ALL. In addition, we cultured the RPMI-8402, Jurkat, Ramos, and Daudi cell lines and assessed the effects of internal (hypoxia) and external (chemotherapy medications L-asparaginase [ASP] and vincristine [VCR]) factors on h19 expression. The expressions of H19, P53, c-Myc, HIF-1α and β-actin were performed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) method.
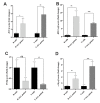
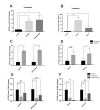
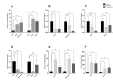
Results: There was significantly increased H19 expression in the B-cell ALL (B-ALL, P<0.05), T-cell ALL (T-ALL, P<0.01) patients and the cell lines. This upregulation was governed by the P53, HIF-1α, and c-Myc transcription factors. We observed that increased c-Myc expression induced H19 expression; however, P53 adversely affected H19 expression. In addition, the results indicated that chemotherapy changed the gene expression pattern. There was a considerable decrease in H19 expression after exposure to chemotherapy medications; nonetheless, hypoxia induced H19 expression through P53 downregulation.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that H19 may have an important role in pathogenesis in ALL and may act as a promising and potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; H19; Hypoxia; lncRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia induces H19 expression through direct and indirect Hif-1α activity, promoting oncogenic effects in glioblastoma.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 22;7:45029. doi: 10.1038/srep45029. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28327666 Free PMC article.
-
Increased level of long non coding RNA H19 is correlated with the downregulation of miR-326 and BCL-2 genes in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a possible hallmark for leukemogenesis.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Feb;48(2):1531-1538. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06161-y. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33580459
-
c-Myc-induced, long, noncoding H19 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer.Med Oncol. 2014 May;31(5):914. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0914-7. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24671855
-
[Differential Expression of Long Non-coding RNA Cancer Susceptibility Candidate 2 and Imprinted Gene H19 in Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022 Feb;44(1):72-80. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.14039. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35300768 Chinese.
-
Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates viability and metastasis, and is upregulated in retinoblastoma.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jun;15(6):8424-8432. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8385. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29805578 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Plasma long non-coding RNAs as biomarkers for bone marrow infiltration and stage in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241292665. doi: 10.1177/03946320241292665. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39393794 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant Expression of Non-Coding RNAs in Pediatric T Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Their Potential Application as Biomarkers.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;16(4):420. doi: 10.3390/genes16040420. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Levels of miRNA-1290 and lncRNA-H19 in Exosomes of Patients Recently Diagnosed With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.In Vivo. 2025 Jul-Aug;39(4):1941-1964. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13993. In Vivo. 2025. PMID: 40579001 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA Signatures in Lymphopoiesis and Lymphoid Malignancies.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Aug 1;9(4):44. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9040044. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37624036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased H19/miR-675 Expression in Adult T-Cell Leukemia Is Associated with a Unique Notch Signature Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 8;25(10):5130. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105130. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Kramer JL, Rowland JH, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(4):271–289. - PubMed
-
- Kang MH, Kang YH, Szymanska B, Wilczynska-Kalak U, Sheard MA, Harned TM, et al. Activity of vincristine, L-ASP, and dexamethasone against acute lymphoblastic leukemia is enhanced by the BH3-mimetic ABT-737 in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2007;110(6):2057–2066. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
