TEA Domain Transcription Factor 1 Inhibits Ferroptosis and Sorafenib Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 36680650
- PMCID: PMC10293458
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-023-07824-5
TEA Domain Transcription Factor 1 Inhibits Ferroptosis and Sorafenib Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
Background: Ferroptosis, as a unique form of cell death, plays crucial negative roles in tumorigenesis and progression. This study aimed to investigate the role and molecular mechanism of TEA domain transcription factor 1 (TEAD1) in HCC and its effect on sorafenib-induced ferroptosis.
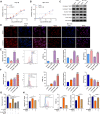
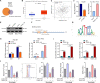
Methods: TEAD1 expression was analyzed in HCC tissues using quantitative PCR, and western blot. The effects on cell proliferation, migration and invasion were determined by CCK-8, wound healing and Transwell assays. Intracellular iron, reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA) and GSH measurement was used to assess ferroptosis. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter gene assays were performed to verify the relationship between TEAD1 and solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2). Expression of mTOR, ribosomal protein S6, glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) and SLC3A2 was analyzed by western blot. Tumor xenografts were used assess the effect of TEAD1 on tumor growth in vivo.
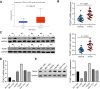
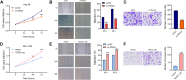
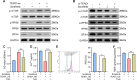
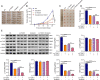
Results: TEAD1 was more abundant in HCC compared with normal tissues. Overexpression of TEAD1 enhanced the proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells, while knockdown of TEAD1 inhibited these cell behaviors. Further, TEAD1 inhibited ferroptosis, which was demonstrated by decreased intracellular Fe2+ content, ROS, and MDA levels, and increased GSH activity. Mechnistically, TEAD1 promotes the transcription of SLC3A2 and activates the mTOR signaling. Additionally, silenced TEAD1 restrained tumor growth and enhance sorafenib-induced antitumor activity in vivo.
Conclusions: TEAD1 confers resistance of HCC cells to ferroptosis, thereby promoting the progression of HCC, suggesting the potential value of TEAD1 in the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
Keywords: Ferroptosis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; TEA domain transcription factor 1; Transcriptional regulation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polyphyllin I induced ferroptosis to suppress the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through activation of the mitochondrial dysfunction via Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 axis.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jan;122:155135. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155135. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 37856990
-
Overexpression of transcription factor TBX5 inhibits the activation of YAP1-TEAD1 pathway to promote ferroptosis in lung cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Jul 23;718:150037. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150037. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38735135
-
Silencing lncRNA HCG18 regulates GPX4-inhibited ferroptosis by adsorbing miR-450b-5p to avert sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2023 Jan-Dec;42:9603271221142818. doi: 10.1177/09603271221142818. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36786348
-
Upregulation of lncRNA NIFK-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma by m6A methylation promotes disease progression and sorafenib resistance.Hum Cell. 2021 Nov;34(6):1800-1811. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00587-z. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34374933 Review.
-
Roles and Mechanisms of Ferroptosis in Sorafenib Resistance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Dec 19;11:2493-2504. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S500084. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39717509 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CENPA-driven STMN1 Transcription Inhibits Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023 Oct 28;11(5):1118-1129. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00034. Epub 2023 Jun 12. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37577230 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis resistance in cancer cells: nanoparticles for combination therapy as a solution.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 19;15:1416382. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1416382. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38962305 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

