Spatiotemporal dissection of tumor microenvironment via in situ sensing and monitoring in tumor-on-a-chip
- PMID: 36680970
- PMCID: PMC9918721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115064
Spatiotemporal dissection of tumor microenvironment via in situ sensing and monitoring in tumor-on-a-chip
Abstract
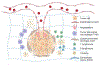
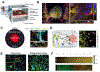
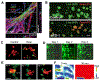
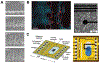
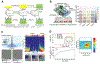
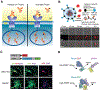
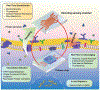
Real-time monitoring in the tumor microenvironment provides critical insights of cancer progression and mechanistic understanding of responses to cancer treatments. However, clinical challenges and significant questions remain regarding assessment of limited clinical tissue samples, establishment of validated, controllable pre-clinical cancer models, monitoring of static versus dynamic markers, and the translation of insights gained from in vitro tumor microenvironments to systematic investigation and understanding in clinical practice. State-of-art tumor-on-a-chip strategies will be reviewed herein, and emerging real-time sensing and monitoring platforms for on-chip analysis of tumor microenvironment will also be examined. The integration of the sensors with tumor-on-a-chip platforms to provide spatiotemporal information of the tumor microenvironment and the associated challenges will be further evaluated. Though optimal integrated systems for in situ monitoring are still in evolution, great promises lie ahead that will open new paradigm for rapid, comprehensive analysis of cancer development and assist clinicians with powerful tools to guide the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment course in cancer.
Keywords: In situ biosensing; Integrated system; Real-time monitoring; Spatiotemporal analysis; Tumor microenvironment; Tumor-on-a-chip.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

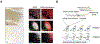
Similar articles
-
Integrated Electrochemical and Optical Biosensing in Organs-on-Chip.Chembiochem. 2024 Feb 1;25(3):e202300560. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202300560. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 37966365 Review.
-
Monitoring immune responses in the tumor microenvironment.Curr Opin Immunol. 2016 Aug;41:23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 May 27. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27240055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosensor-Enhanced Organ-on-a-Chip Models for Investigating Glioblastoma Tumor Microenvironment Dynamics.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;24(9):2865. doi: 10.3390/s24092865. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-on-a-chip for integrating a 3D tumor microenvironment: chemical and mechanical factors.Lab Chip. 2020 Mar 3;20(5):873-888. doi: 10.1039/c9lc00550a. Lab Chip. 2020. PMID: 32025687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy discovery on tumor organoid-on-a-chip platforms that recapitulate the tumor microenvironment.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Aug;187:114365. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114365. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35667465 Review.
Cited by
-
The tumor microenvironment across four dimensions: assessing space and time in cancer biology.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1554114. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1554114. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40625731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving tumor microenvironment assessment in chip systems through next-generation technology integration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 25;12:1462293. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1462293. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39386043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A nanoplasmonic cell-on-a-chip for in situ monitoring of PD-L1+ exosome-mediated immune modulation.Biosens Bioelectron. 2025 Jun 1;277:117293. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2025.117293. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Biosens Bioelectron. 2025. PMID: 39999609
-
S2Map: a novel computational platform for identifying secretio-types through cell secretion-signal map.Bioinform Adv. 2025 Mar 20;5(1):vbaf059. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbaf059. eCollection 2025. Bioinform Adv. 2025. PMID: 40191548 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Experimental Models of Colorectal Cancer: A Critical Appraisal from 2D Cell Systems to Organoids, Humanized Mouse Avatars, Organ-on-Chip, CRISPR Engineering, and AI-Driven Platforms-Challenges and Opportunities for Translational Precision Oncology.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;17(13):2163. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132163. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647462 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

