Inflammasomes cross-talk with lymphocytes to connect the innate and adaptive immune response
- PMID: 36681114
- PMCID: PMC10703620
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.01.012
Inflammasomes cross-talk with lymphocytes to connect the innate and adaptive immune response
Abstract
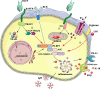
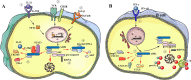
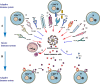
Background: Innate and adaptive immunity are two different parts of the immune system that have different characteristics and work together to provide immune protection. Inflammasomes are a major part of the innate immune system that are expressed widely in myeloid cells and are responsible for inflammatory responses. Recent studies have shown that inflammasomes are also expressed and activated in lymphocytes, especially in T and B cells, to regulate the adaptive immune response. Activation of inflammasomes is also under the control of lymphocytes. Therefore, we propose that inflammasomes act as a bridge and they provide crosstalk between the innate and adaptive immune systems to obtain a fine balance in immune responses.
Aim of review: This review systematially summarizes the interaction between inflammasomes and lymphocytes and describes the crosstalk between the innate and adaptive immune systems induced by inflammasomes, with the aim of providing new directions and important areas for further research.
Key scientific concepts of review: When considering the novel function of inflammasomes in various lymphocytes, attention should be given to the activity of specific inflammasomes in studies of lymphocyte function. Moreover, research on the function of various inflammasomes in lymphocytes will help advance knowledge on the mechanisms and treatment of various diseases, including autoimmune diseases and tumors. In addition, when studying inflammatory responses, inflammasomes in both lymphocytes and myeloid cells need to be considered.
Keywords: AIM2; Adaptive immunity; Inflammasome; Innate immunity; Lymphocyte; NLRP3.
Copyright © 2023. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolism-inflammasome crosstalk shapes innate and adaptive immunity.Cell Chem Biol. 2024 May 16;31(5):884-903. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2024.04.006. Cell Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38759617 Review.
-
Inflammasomes and adaptive immune responses.Nat Immunol. 2021 Apr;22(4):412-422. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00869-6. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Nat Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33603227 Review.
-
From autoinflammation to autoimmunity: old and recent findings.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Sep;37(9):2305-2321. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4209-9. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 30014358 Review.
-
Inflammasome, T Lymphocytes and Innate-Adaptive Immunity Crosstalk: Role in Cardiovascular Disease and Therapeutic Perspectives.Thromb Haemost. 2018 Aug;118(8):1352-1369. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1666860. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29991092 Review.
-
Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory bowel diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 7;25(33):4796-4804. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4796. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31543674 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Immune-Stimulating and Anti-Diabetic Effects of Allium hookeri Leaves Grown in a Plant Factory with Artificial Lights in Immunosuppressed Obese C57BL/6 Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 9;17(1):91. doi: 10.3390/ph17010091. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256924 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasomes in lymphocytes as therapeutic targets.Transl Oncol. 2025 Apr;54:102342. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102342. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40054124 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differentially affects pro-inflammatory cell subsets in adipose tissue depots in a diet induced obesity model.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Dec 18;15(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00677-1. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 39696610 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Value of Peri-Coronary Fat Attenuation Index in Elderly Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Its Correlation with Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Apr 18;25(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04730-8. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40251516 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in acute COPD exacerbation: clarifying specific immune mechanisms of infectious and noninfectious factors.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025 Jan-Dec;19:17534666241308408. doi: 10.1177/17534666241308408. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025. PMID: 40098281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deets K.A., Vance R.E. Inflammasomes and adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(4):412–422. - PubMed
-
- Kaur B.P., Secord E. Innate Immunity. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2021;41(4):535–541. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi O., Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010;140(6):805–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

