Cancer-associated fibroblast-secreted IGFBP7 promotes gastric cancer by enhancing tumor associated macrophage infiltration via FGF2/FGFR1/PI3K/AKT axis
- PMID: 36681667
- PMCID: PMC9867714
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-023-01336-x
Cancer-associated fibroblast-secreted IGFBP7 promotes gastric cancer by enhancing tumor associated macrophage infiltration via FGF2/FGFR1/PI3K/AKT axis
Abstract
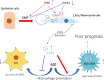
We previously reported that IGFBP7 plays a role in maintaining mRNA stability of oncogenic lncRNA UBE2CP3 by RNA-RNA interaction in gastric cancer (GC). Clinical cohort studies had implied an oncogenic role of IGFBP7 in GC. However, the molecular mechanism of IGFBP7 in GC progression remains unknown. In this study, clinical analysis based on two independent cohorts showed that IGFBP7 was positively associated with poor prognosis and macrophage infiltration in GC. Loss-of-function studies confirmed the oncogenic properties of IGFBP7 in regulating GC cell proliferation and invasion. Mechanismly, IGFBP7 was highly expressed in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) and mesenchymal cells, and was induced by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) signaling, since its expression was increased by TGF-beta treatment and reduced by overexpression of OVOL2 in GC. RNA sequencing, qRT-PCR, ELISA assay showed that IGFBP7 positively regulated FGF2 expression and secretion in GC. Transcriptome analysis revealed that FGFR1 was downregulated in M1 polarization but upregulated in M2 polarization. Exogenous recombinant IGFBP7 treatment in macrophages and GC cells further identified that IGFBP7 promotes tumor associated macrophage (TAM) polarization via FGF2/FGFR1/PI3K/AKT axis. Our finding here represented the first evidence that IGFBP7 promotes GC by enhancing TAM/M2 macrophage polarization through FGF2/FGFR1/PI3K/AKT axis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

