Deep learning can yield clinically useful right ventricular segmentations faster than fully manual analysis
- PMID: 36681759
- PMCID: PMC9867728
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-28348-y
Deep learning can yield clinically useful right ventricular segmentations faster than fully manual analysis
Abstract
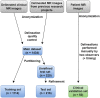
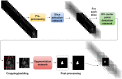
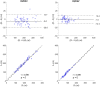
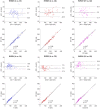
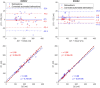
Right ventricular (RV) volumes are commonly obtained through time-consuming manual delineations of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images. Deep learning-based methods can generate RV delineations, but few studies have assessed their ability to accelerate clinical practice. Therefore, we aimed to develop a clinical pipeline for deep learning-based RV delineations and validate its ability to reduce the manual delineation time. Quality-controlled delineations in short-axis CMR scans from 1114 subjects were used for development. Time reduction was assessed by two observers using 50 additional clinical scans. Automated delineations were subjectively rated as (A) sufficient for clinical use, or as needing (B) minor or (C) major corrections. Times were measured for manual corrections of delineations rated as B or C, and for fully manual delineations on all 50 scans. Fifty-eight % of automated delineations were rated as A, 42% as B, and none as C. The average time was 6 min for a fully manual delineation, 2 s for an automated delineation, and 2 min for a minor correction, yielding a time reduction of 87%. The deep learning-based pipeline could substantially reduce the time needed to manually obtain clinically applicable delineations, indicating ability to yield right ventricular assessments faster than fully manual analysis in clinical practice. However, these results may not generalize to clinics using other RV delineation guidelines.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
EH is the CTO and founder of Medviso AB that produces the software Segment that was used throughout this study. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Miao, Y. et al. A right ventricle segmentation method based on U-net with weighted convolution and dense connection. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Medicine and Image Processing 40–46 (ACM, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

