A PK/PD model for the evaluation of clinical rifaximin dosage for the treatment of dairy cow mastitis induced by Escherichia coli
- PMID: 36681807
- PMCID: PMC9863146
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-022-03564-2
A PK/PD model for the evaluation of clinical rifaximin dosage for the treatment of dairy cow mastitis induced by Escherichia coli
Abstract
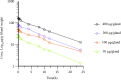
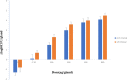
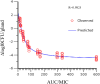
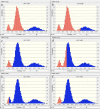
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is an opportunistic pathogen that can cause clinical mastitis in dairy cows worldwide. Mastitis produces severe symptoms in dairy cows, such as udder inflammation, the production of harmful substances, reduced milk production, and altered milk quality. Intramammary injections of rifaximin have a beneficial effect on dairy cow mastitis, especially for mastitis caused by E. coli. However, we do not know whether the currently accepted clinical administration scheme is reasonable. Therefore, the purpose of this experiment was to evaluate the clinical dosing regimen for curing mastitis induced by E. coli. In this study, the pharmacokinetics of four single dose groups (50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/gland) were studied in CD-1 lactating mice, and the main pharmacokinetic parameters were obtained by non-compartment and two-compartment model of Phoenix 8.1 software. A total of 5,000 colony-forming units (CFU) of E. coli ATCC25922 were injected into the mammary glands of mice under anatomic microscope guidance. After 12 h of growth in vivo, the mouse mastitis model was successfully developed. In pharmacodynamics experiment, 12 different dosing regimens (doses ranged from 25 to 800 µg/gland and two dosing intervals of 12 and 24 h) were used to study the therapeutic potential of rifaximin for mastitis. The PK/PD model was established by integrating pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics using the inhibitory sigmoid Emax model. The optimal antibacterial effect was 2log10CFU/gland reduction of bacterial colony counts in vivo, when the magnitude of AUC24/MIC exceeded 57.80 h. A total of 57.80 h of AUC24/MIC was defined as a target value in the Monte Carlo simulation. The clinically recommended dosage regimen of 100 mg/gland every 12 h in a day achieved a 91.08% cure rate for the treatment of bovine mastitis caused by E. coli infection.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Mastitis; Monte Carlo simulation; PK/PD model; Rifaximin.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PK/PD Modeling to Assess Rifaximin Clinical Dosage in a Mouse Model of Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Mastitis.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Jun 14;8:651369. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.651369. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34195244 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of antibiotic versus no treatment at dry-off on udder health and milk yield in subsequent lactation: A retrospective analysis of Austrian health recording data from dairy herds.J Dairy Sci. 2023 Jan;106(1):452-461. doi: 10.3168/jds.2022-21790. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Dairy Sci. 2023. PMID: 36333135
-
PK/PD integration and pharmacodynamic cutoff of cefquinome against cow mastitis due to Escherichia coli.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jan;45(1):83-91. doi: 10.1111/jvp.13012. Epub 2021 Sep 1. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34469000
-
Severity of E. coli mastitis is mainly determined by cow factors.Vet Res. 2003 Sep-Oct;34(5):521-64. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2003023. Vet Res. 2003. PMID: 14556694 Review.
-
Treatment for bovine Escherichia coli mastitis - an evidence-based approach.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Dec;36(6):521-31. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12057. Epub 2013 May 17. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23679229 Review.
Cited by
-
Rifaximin resistance in Clostridioides difficile is associated with specific rpoB alleles and multilocus sequence typing (MLST) clades.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Jul 29;25(1):458. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04164-4. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40731265 Free PMC article.
-
Profile of circular RNAs in bovine mammary tissues infected with Staphylococcus aureus.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Feb 21;207(3):67. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04269-4. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39982455
References
-
- Dieter D, Koen B, Guido S, Evelyne M. Short communication: Antimicrobial efficacy of intramammary treatment with a novel biphenomycin compound against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus uberis, and Escherichia coli -induced mouse mastitis. J Dairy Sci. 2013;96(11):7082–7087. doi: 10.3168/jds.2013-7011. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

