Mechanism of immune infiltration in synovial tissue of osteoarthritis: a gene expression-based study
- PMID: 36681837
- PMCID: PMC9862811
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-023-03541-x
Mechanism of immune infiltration in synovial tissue of osteoarthritis: a gene expression-based study
Abstract
Background: Osteoarthritis is a chronic degenerative joint disease, and increasing evidences suggest that the pathogenic mechanism involves immune system and inflammation.
Aims: The aim of current study was to uncover hub genes linked to immune infiltration in osteoarthritis synovial tissue using comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and experimental confirmation.
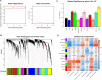
Methods: Multiple microarray datasets (GSE55457, GSE55235, GSE12021 and GSE1919) for osteoarthritis in Gene Expression Omnibus database were downloaded for analysis. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using Limma package in R software, and immune infiltration was evaluated by CIBERSORT algorithm. Then weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was performed to uncover immune infiltration-associated gene modules. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed to select the hub genes, and the tissue distribution of these genes was analyzed using BioGPS database. Finally, the expression pattern of these genes was confirmed by RT-qPCR using clinical samples.
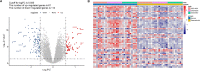
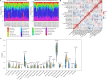
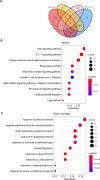
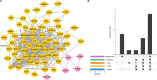
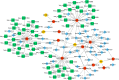
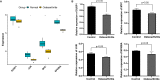
Results: Totally 181 DEGs between osteoarthritis and normal control were screened. Macrophages, mast cells, memory CD4 T cells and B cells accounted for the majority of immune cell composition in synovial tissue. Osteoarthritis synovial showed high abundance of infiltrating resting mast cells, B cells memory and plasma cells. WGCNA screened 93 DEGs related to osteoarthritis immune infiltration. These genes were involved in TNF signaling pathway, IL-17 signaling pathway, response to steroid hormone, glucocorticoid and corticosteroid. Ten hub genes including MYC, JUN, DUSP1, NFKBIA, VEGFA, ATF3, IL-6, PTGS2, IL1B and SOCS3 were selected by using PPI network. Among them, four genes (MYC, JUN, DUSP1 and NFKBIA) specifically expressed in immune system were identified and clinical samples revealed consistent change of these four genes in synovial tissue retrieved from patients with osteoarthritis.
Conclusion: A 4-gene-based diagnostic model was developed, which had well predictive performance in osteoarthritis. MYC, JUN, DUSP1 and NFKBIA might be biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets in osteoarthritis.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Immune infiltration; Osteoarthritis; Synovial; Weighed gene co-expression network analysis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis by bioinformatics analysis.PeerJ. 2020 Jan 17;8:e8390. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8390. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 31988808 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration and Identification of Potential Biomarkers and Immune Cell Infiltration Analysis in Synovial Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2025 Feb;28(2):e70137. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.70137. Int J Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 39953769
-
Screening and identification of potential hub genes and immune cell infiltration in the synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis by bioinformatic approach.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 10;9(1):e12799. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12799. eCollection 2023 Jan. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36699262 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Disease-Specific Hub Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Tissues by Bioinformatics Analysis.Dis Markers. 2021 May 17;2021:9911184. doi: 10.1155/2021/9911184. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34113405 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the Hub Genes and Immune Cell Infiltration in Synovial Tissue between Osteoarthritic and Rheumatoid Arthritic Patients by Bioinformatic Approach.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(6):497-509. doi: 10.2174/1381612827666211104154459. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 34736376
Cited by
-
Integrated bioinformatics and clinical data identify three novel biomarkers for osteoarthritis diagnosis and synovial immune.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 31;15(1):10987. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95837-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40164659 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Bioinformatics and Experimental Validation Reveal Macrophage Polarization-Related Biomarkers for Osteoarthritis Diagnosis.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 Aug 1;18:4589-4612. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S537507. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40765736 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Insights into the Regulatory Role of N6-Methyladenosine in the Pathogenesis and Clinical Treatment of Osteoarthritis: Research Status and Prospect.J Inflamm Res. 2025 May 27;18:6749-6766. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S508973. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40453975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of TNF signaling pathway-related genes in knee osteoarthritis (KOA) using WGCNA and machine learning.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 15;104(33):e43849. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043849. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40826778 Free PMC article.
-
[Identification of Characteristic lncRNA Molecular Markers in Osteoarthritis by Integrating GEO Database and Machine Learning Strategies and Experimental Validation].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Sep;54(5):899-907. doi: 10.12182/20230960101. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37866944 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

