Genetic control of RNA editing in neurodegenerative disease
- PMID: 36681936
- PMCID: PMC10387301
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbad007
Genetic control of RNA editing in neurodegenerative disease
Abstract
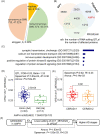
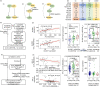
A-to-I RNA editing diversifies human transcriptome to confer its functional effects on the downstream genes or regulations, potentially involving in neurodegenerative pathogenesis. Its variabilities are attributed to multiple regulators, including the key factor of genetic variants. To comprehensively investigate the potentials of neurodegenerative disease-susceptibility variants from the view of A-to-I RNA editing, we analyzed matched genetic and transcriptomic data of 1596 samples across nine brain tissues and whole blood from two large consortiums, Accelerating Medicines Partnership-Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative. The large-scale and genome-wide identification of 95 198 RNA editing quantitative trait loci revealed the preferred genetic effects on adjacent editing events. Furthermore, to explore the underlying mechanisms of the genetic controls of A-to-I RNA editing, several top RNA-binding proteins were pointed out, such as EIF4A3, U2AF2, NOP58, FBL, NOP56 and DHX9, since their regulations on multiple RNA-editing events were probably interfered by these genetic variants. Moreover, these variants may also contribute to the variability of other molecular phenotypes associated with RNA editing, including the functions of 3 proteins, expressions of 277 genes and splicing of 449 events. All the analyses results shown in NeuroEdQTL (https://relab.xidian.edu.cn/NeuroEdQTL/) constituted a unique resource for the understanding of neurodegenerative pathogenesis from genotypes to phenotypes related to A-to-I RNA editing.
Keywords: A-to-I RNA editing; RNA editing quantitative trait loci; RNA-binding protein; mediation analysis; neurodegenerative disease.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Genetic variation and microRNA targeting of A-to-I RNA editing fine tune human tissue transcriptomes.Genome Biol. 2021 Mar 9;22(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02287-1. Genome Biol. 2021. PMID: 33685485 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of biological networks and the eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-3 gene as pivotal in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Biochem. 2020 Oct;121(10):4094-4107. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29596. Epub 2020 Jan 3. J Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31898336
-
Hsa_circ_0004296 inhibits metastasis of prostate cancer by interacting with EIF4A3 to prevent nuclear export of ETS1 mRNA.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Oct 25;40(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02138-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34696782 Free PMC article.
-
A targeted approach: Gene and RNA editing for neurodegenerative disease treatment.Life Sci. 2025 Sep 1;376:123756. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123756. Epub 2025 May 22. Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40412606 Review.
-
Contribution of A-to-I RNA editing, M6A RNA Methylation, and Alternative Splicing to physiological brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases.Mech Ageing Dev. 2023 Jun;212:111807. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2023.111807. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Mech Ageing Dev. 2023. PMID: 37023929 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA editing enzymes: structure, biological functions and applications.Cell Biosci. 2024 Mar 16;14(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01216-6. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38493171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Regulation of A-to-I RNA Editing on Genes in Parkinson's Disease.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 15;14(4):919. doi: 10.3390/genes14040919. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behm M, Öhman M. RNA editing: a contributor to neuronal dynamics in the mammalian brain. Trends Genet 2016;32:165–75. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg E, Levanon EY. A-to-I RNA editing—immune protector and transcriptome diversifier. Nat Rev Genet 2018;19:473–90. - PubMed
-
- Lomeli H, Mosbacher J, Melcher T, et al. Control of kinetic properties of AMPA receptor channels by nuclear RNA editing. Science 1994;266:1709–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

