Identification of a short ACE2-derived stapled peptide targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
- PMID: 36682293
- PMCID: PMC9842534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115118
Identification of a short ACE2-derived stapled peptide targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
Abstract
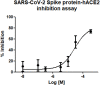
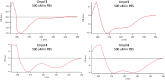
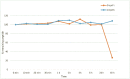
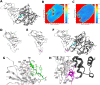
The design and synthesis of a series of peptide derivatives based on a short ACE2 α-helix 1 epitope and subsequent [i - i+4] stapling of the secondary structure resulted in the identification of a 9-mer peptide capable to compete with recombinant ACE2 towards Spike RBD in the micromolar range. Specifically, SARS-CoV-2 Spike inhibitor screening based on colorimetric ELISA assay and structural studies by circular dichroism showed the ring-closing metathesis cyclization being capable to stabilize the helical structure of the 9-mer 34HEAEDLFYQ42 epitope better than the triazole stapling via click chemistry. MD simulations showed the stapled peptide being able not only to bind the Spike RBD, sterically interfering with ACE2, but also showing higher affinity to the target as compared to parent epitope.
Keywords: COVID-19; Infectious diseases; Molecular modeling; Peptidomimetics; Protein-protein interaction; Ring-closing metathesis.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
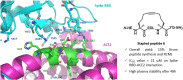
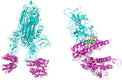
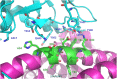
Similar articles
-
Computational Design and Experimental Validation of ACE2-Derived Peptides as SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Inhibitors.J Phys Chem B. 2022 Oct 20;126(41):8129-8139. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.2c03918. Epub 2022 Oct 11. J Phys Chem B. 2022. PMID: 36219223
-
Peptidomimetic Small-Molecule Inhibitors of 3CLPro Activity and Spike-ACE2 Interaction: Toward Dual-Action Molecules against Coronavirus Infections.J Org Chem. 2022 Sep 16;87(18):12041-12051. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c01047. Epub 2022 Aug 30. J Org Chem. 2022. PMID: 36039955 Free PMC article.
-
Stapled Peptides Based on Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Potently Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infection In Vitro.mBio. 2020 Dec 11;11(6):e02451-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02451-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33310780 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive SARS-CoV-2 Serology Reveals Most Antibodies Targeting the Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Compete for ACE2 Binding.mSphere. 2020 Sep 16;5(5):e00802-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00802-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32938700 Free PMC article.
-
Stapled peptides as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the hACE2 receptor.J Pept Sci. 2022 Sep;28(9):e3409. doi: 10.1002/psc.3409. Epub 2022 Feb 26. J Pept Sci. 2022. PMID: 35165970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2 of Conformationally Constrained Helical Peptides Derived from Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2.ACS Omega. 2023 Jun 13;8(25):22665-22672. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01436. eCollection 2023 Jun 27. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37387789 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Structural Flexibility in Hydrocarbon-Stapled Peptides Designed to Block Viral Infection via Human ACE2 Mimicry.Pept Sci (Hoboken). 2024 Nov;116(6):e24375. doi: 10.1002/pep2.24375. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Pept Sci (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 39866902
-
Novel Polymyxin-Inspired Peptidomimetics Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Spike:hACE2 Interface.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 15;24(10):8765. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108765. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240111 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2024 Mar 14;67(5):3205-3231. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01543. Epub 2024 Feb 23. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38394369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
-
- Worldometer, Cases Coronavirus. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/coronavirus-cases/#daily-cases
-
- Callaway E. Beyond Omicron: what's next for COVID's viral evolution. Nature. 2021;600:204–207. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

